Create the service interceptor project in IntelliJ
This walk-through demonstrates how to create, build, and deploy a service interceptor using IntelliJ IDEA. Before you begin, ensure that all prerequisites mentioned in systems requirements are installed on your development machine.
To create a service interceptor project using IntelliJ, complete the following steps:
-
Launch IntelliJ and go to File > New > Project.
-
Under Generators, select Maven Archetype.
-
Enter AuditLogInterceptor in the Name field.
-
In the Location field, specify a location on the machine where you want to store the project.
-
Choose JDK 17 from the JDK drop-down menu.
-
Under Catalog, ensure that the default internal catalog is selected.
-
For Archetype
Click the Add... button on the right, and type the following values in the Add Archetype wizard, and then click Add:
- GroupId:
com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.sdk - ArtifactId:
server-services-interceptor-archetype - Version:
12.0.0

The server-services-interceptor-archetype has been added. Once you add the archetype,
interceptorwill appear under Additional Properties.Name - GroupId:
-
To configure advanced settings, expand Advanced Settings and provide the required information.

-
Click Create and a new service interceptor project is created. You should see
Build Successon the right of the bottom Run Tool Window.
If you see any warnings, you can ignore them as long as the project has successfully generated the Audit class in the \src\main\java folder. Those warnings will be addressed during the project build.
Modify the code and package the service interceptor project
Building the service interceptor project will package the project’s classes, dependencies, and resources into a .interceptor file, which can be deployed to ArcGIS Server. Since it’s a Maven project, the Maven build lifecycle must be followed to build the service interceptor.
You can build the service interceptor project from either the Maven tool window or the Terminal tool window.
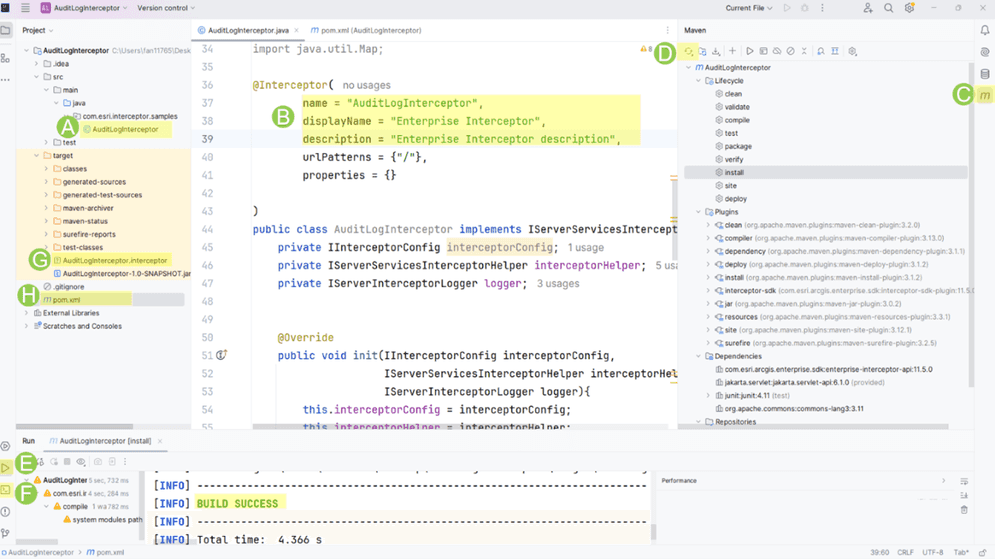
Since the project is created from server-services-interceptor-archetype, it automatically loads the boilerplate code that implements a ready-to-use service interceptor.
-
Open the
Auditclass located inLog Interceptor src\main\java(see A in above image). -
Copy and paste the following code into the
Auditclass.Log Interceptor.java Use dark colors for code blocks Copy import com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.interceptor.Interceptor; import com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.interceptor.server.IServerServicesInterceptor; import com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.interceptor.IInterceptorRequest; import com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.interceptor.IInterceptorResponse; import com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.interceptor.server.IServerServicesInterceptorChain; import com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.interceptor.server.IServerServicesInterceptorHelper; import com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.interceptor.IInterceptorConfig; import com.esri.arcgis.enterprise.interceptor.server.IServerInterceptorLogger; import jakarta.servlet.ServletException; import java.io.IOException; @Interceptor( name = "AuditLogInterceptor", displayName = "Audit Log Interceptor", description = "Audit Log Interceptor", urlPatterns = {"/MapServer/","/FeatureServer/"}, properties = {"prop1=value1"}, chainingOrder = 1 ) public class AuditLogInterceptor implements IServerServicesInterceptor { private IServerServicesInterceptorHelper interceptorHelper; private IServerInterceptorLogger logger; @Override public void init(IInterceptorConfig interceptorConfig, IServerServicesInterceptorHelper interceptorHelper, IServerInterceptorLogger logger){ // This code executes at the time of registration this.interceptorHelper = interceptorHelper; this.logger = logger; } @Override public void intercept( IInterceptorRequest request, IInterceptorResponse response, IServerServicesInterceptorChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { // Continue the chain if it's not REST request if (!filterChain.isRestRequestChain()) { filterChain.intercept(request, response); return; } //To intercept the request, write your code here logUserAction(request, response); filterChain.intercept(request, response); //To intercept the response, write your code here } /* * Perform any cleanup required by the interceptor at the end of its lifecycle */ @Override public void cleanup() { } private void logUserAction(IInterceptorRequest request, IInterceptorResponse response) { String username = interceptorHelper.getUsername(request, response); String serviceName = interceptorHelper.getServiceName(request, response); String serviceType = interceptorHelper.getServiceType(request, response); String serviceProvider= interceptorHelper.getServiceProviderType(request, response); String operationName = interceptorHelper.getOperationName(request, response); String msg = "User '" + username + "' " + "accessed the service " + serviceName + "." + serviceType + ". " + "Service provider is " + serviceProvider + ". " + ((operationName != null && !operationName.isEmpty()) ? "Performed the operation - '" + operationName + "'." : ""); logger.info(msg); } } -
Set the
displayandName descriptionof your choice (see B in above image). -
Follow these steps to build the project from the Maven tool window:
-
On the toolbar on the right, click Maven (see C in above image). The Maven tool window appears.
-
Expand
Audit.UnderLog Interceptor Audit, you should see the Lifecycle, Plugins, and Dependencies sections. If you do not see the Dependencies section, click Reimport All Maven Projects on the top left of the Maven tool window (see D in above image).Log Interceptor -
Expand Lifecycle and click install. You can also click clean and then click install for a clean build of the project. The project is built successfully with detailed log messages in the Run tool window (see E in above image).
Alternatively, follow these steps to build the project from the Terminal tool window.
-
On the toolbar on the right, click the Terminal (see F in above image).
-
Ensure the directory is pointing to the project's root directory.
-
Type
mvn clean install. This command does a clean build of the project, and you should seeBuild Success.
-
-
Once the build is complete, a new folder named target appears in the project's root directory, where you can find the
Auditfile (see G in above image).Log Interceptor.interceptor
If you want to add third-party libraries as dependencies, you can add them to the project's pom.xml (see H). The POM contains project configuration information, including the Java compiler (JDK) and plug-ins used, as well as the project version and dependencies. To learn more about POM dependency management.
Deploy the service interceptor in ArcGIS Server
To deploy the service interceptor in ArcGIS Server, first upload the interceptor and then register the interceptor.