Analyze the viewshed for an object (geo element) in a scene.
Use case
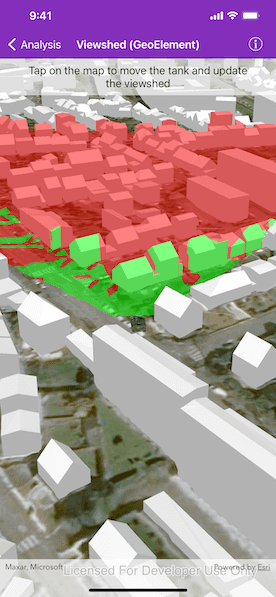
A viewshed analysis is a type of visual analysis you can perform on a scene. The viewshed aims to answer the question 'What can I see from a given location?'. The output is an overlay with two different colors - one representing the visible areas (green) and the other representing the obstructed areas (red).
How to use the sample
Tap to set a destination for the vehicle (an AGSGeoElement). The vehicle will 'drive' towards the tapped location. The viewshed analysis will update as the vehicle moves.
How it works
- Create and show the scene, with an elevation source and a buildings layer.
- Add an
AGSModelSceneSymbol(the GeoElement) to represent the observer (in this case, a tank).- Use an
AGSSimpleRendererwhich has a heading expression set in theAGSRendererSceneProperties. This way you can relate the viewshed's heading to the object's heading.
- Use an
- Create an
AGSGeoElementViewshedwith configuration for the viewshed analysis. - Add the viewshed to an
AGSAnalysisOverlayand add the overlay to the scene. - Configure the SceneView
AGSCameraControllerto orbit the vehicle.
Relevant API
- AGSAnalysisOverlay
- AGSGeodeticDistanceResult
- AGSGeoElementViewshed
- AGSGeometryEngine
- AGSModelSceneSymbol
- AGSOrbitGeoElementCameraController
Offline data
Model Marker Symbol Data will be downloaded by the sample viewer automatically.
About the data
This sample shows a Johannesburg, South Africa Scene from ArcGIS Online. The sample uses a Tank model scene symbol hosted as an item on ArcGIS Online.
Tags
3D, analysis, buildings, model, scene, viewshed, visibility analysis
Sample Code
// Copyright 2017 Esri.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
import UIKit
import ArcGIS
class ViewshedGeoElementViewController: UIViewController, AGSGeoViewTouchDelegate {
@IBOutlet var sceneView: AGSSceneView!
var tank = AGSGraphic()
var waypoint: AGSPoint?
var animationTimer: Timer?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Add the source code button item to the right of navigation bar
(navigationItem.rightBarButtonItem as! SourceCodeBarButtonItem).filenames = ["ViewshedGeoElementViewController"]
// set the sceneView's touch delegate so we can get user taps
sceneView.touchDelegate = self
let graphicsOverlay = makeGraphicsOverlay()
sceneView.graphicsOverlays.add(graphicsOverlay)
let analysisOverlay = makeAnalysisOverlay()
sceneView.analysisOverlays.add(analysisOverlay)
let cameraController = makeCameraController()
sceneView.cameraController = cameraController
sceneView.scene = makeScene()
}
private func makeScene() -> AGSScene {
// create the scene
let scene = AGSScene(basemapStyle: .arcGISImagery)
// add base surface for elevation data
let surface = AGSSurface()
/// The url of the image service for elevation in Brest, France.
let brestElevationServiceURL = URL(string: "https://scene.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/BREST_DTM_1M/ImageServer")!
let elevationSource = AGSArcGISTiledElevationSource(url: brestElevationServiceURL)
surface.elevationSources.append(elevationSource)
scene.baseSurface = surface
/// The url of the scene service for buildings in Brest, France.
let brestBuildingsServiceURL = URL(string: "https://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P3ePLMYs2RVChkJx/arcgis/rest/services/Buildings_Brest/SceneServer/layers/0")!
// add a scene layer
let buildings = AGSArcGISSceneLayer(url: brestBuildingsServiceURL)
scene.operationalLayers.add(buildings)
return scene
}
private func makeGraphicsOverlay() -> AGSGraphicsOverlay {
// create a graphics overlay for the tank
let graphicsOverlay = AGSGraphicsOverlay()
graphicsOverlay.sceneProperties = AGSLayerSceneProperties(surfacePlacement: .relative)
// set up heading expression for tank
let renderer3D = AGSSimpleRenderer()
let sceneProperties = AGSRendererSceneProperties(headingExpression: "[heading] + 90", pitchExpression: "[pitch]", rollExpression: "[roll]")
sceneProperties.headingExpression = "[HEADING]"
renderer3D.sceneProperties = sceneProperties
graphicsOverlay.renderer = renderer3D
// create a graphic of a tank
let tankSymbol = AGSModelSceneSymbol(name: "bradle", extension: "3ds", scale: 10.0)
tankSymbol.heading = 90.0
tankSymbol.anchorPosition = .bottom
tank = AGSGraphic(
geometry: AGSPoint(x: -4.506390,
y: 48.385624,
spatialReference: .wgs84()),
symbol: tankSymbol,
attributes: ["HEADING": 0.0]
)
graphicsOverlay.graphics.add(tank)
return graphicsOverlay
}
private func makeAnalysisOverlay() -> AGSAnalysisOverlay {
// create a viewshed to attach to the tank
let geoElementViewshed = AGSGeoElementViewshed(
geoElement: tank,
horizontalAngle: 90.0,
verticalAngle: 40.0,
minDistance: 0.1,
maxDistance: 250.0,
headingOffset: 0.0,
pitchOffset: 0.0
)
// offset viewshed observer location to top of tank
geoElementViewshed.offsetZ = 3.0
// create an analysis overlay to add the viewshed to the scene view
let analysisOverlay = AGSAnalysisOverlay()
analysisOverlay.analyses.add(geoElementViewshed)
return analysisOverlay
}
private func makeCameraController() -> AGSCameraController {
// set camera controller to follow tank
let cameraController = AGSOrbitGeoElementCameraController(targetGeoElement: tank, distance: 200.0)
cameraController.cameraPitchOffset = 45.0
return cameraController
}
func geoView(_ geoView: AGSGeoView, didTapAtScreenPoint screenPoint: CGPoint, mapPoint: AGSPoint) {
// set the new waypoint
waypoint = mapPoint
// start a timer to animate towards the waypoint
animationTimer = Timer.scheduledTimer(withTimeInterval: 0.1, repeats: true) { [weak self] _ in
self?.animate()
}
}
private func animate() {
guard let waypoint = waypoint,
let location = tank.geometry as? AGSPoint else { return }
guard let distanceResult = AGSGeometryEngine.geodeticDistanceBetweenPoint1(location,
point2: waypoint,
distanceUnit: AGSLinearUnit.meters(),
azimuthUnit: AGSAngularUnit.degrees(),
curveType: .geodesic) else { return }
// move toward waypoint a short distance
let locations = AGSGeometryEngine.geodeticMove([location],
distance: 1.0,
distanceUnit: AGSLinearUnit.meters(),
azimuth: distanceResult.azimuth1,
azimuthUnit: distanceResult.azimuthUnit ?? AGSAngularUnit.degrees(),
curveType: .geodesic)
if let newLocation = locations?.first {
tank.geometry = newLocation
}
if let heading = tank.attributes["HEADING"] as? Double {
tank.attributes["HEADING"] = heading + ((distanceResult.azimuth1 - heading) / 10)
}
// stop the animation when we're within 5 meters of the waypoint
if distanceResult.distance <= 5 {
self.waypoint = nil
animationTimer?.invalidate()
}
}
}