You can use JavaScript to customize ArcGIS Survey123 surveys by adding custom functions that extend beyond standard XLSForm capabilities. This allows you to implement complex logic, calculations, data validation, and data transformation that would be difficult to achieve with XLSForm expressions alone. This page provides a guide for developers who need to implement business logic, integrate with external data sources, or create reusable functions across multiple surveys.
You use JavaScript functions to:
- Handle data structures and arrays
- Perform string manipulation and parsing
- Implement validation logic
- Create reusable code across multiple surveys
- Process external data through API calls (with limitations)
When to use JavaScript vs XLSForm expressions
Choose the right approach based on your complexity and requirements:
| Feature | XLSForm expressions | JavaScript functions |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Simple to moderate calculations | Complex logic and data processing |
| Reusability | Limited to single survey | Reusable across multiple surveys |
| Data Structures | Basic field references | Arrays, objects, and data |
| String Operations | Basic concatenation and functions | Parsing and manipulation |
| Validation | Simple constraints | Conditional validation |
| Performance | Fast, built-in functions | Slower, custom execution |
| Debugging | Limited error messages | Console logging and errors |
| Use Case | Standard survey logic | Business rules and integration |
Prerequisites
Before using JavaScript customization in a survey, you need:
- Survey123 Connect: JavaScript functions are supported only in surveys authored and published using Survey123 Connect.
- ArcGIS organization account: JavaScript functions are available only to users within the same ArcGIS organization as the survey author.
- JavaScript knowledge: Basic understanding of JavaScript syntax and functions.
- XLSForm experience: Familiarity with XLSForm structure and
pulldata()function.
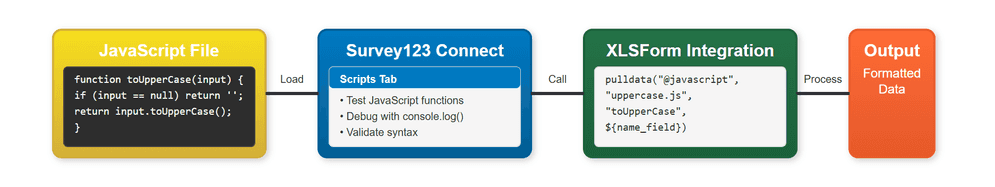
How to customize surveys with JavaScript
To customize surveys with JavaScript, you use Survey123 Connect to create custom JavaScript functions that extend beyond standard XLSForm capabilities. These functions run in a sandboxed environment and can perform complex logic, calculations, and data transformation that would be difficult to achieve with XLSForm expressions alone.
The general steps are:
- Create JavaScript files: Add JavaScript files to your survey project using Survey123 Connect
- Write custom functions: Implement JavaScript functions with proper input parameters and return values
- Reference in XLSForm: Use
pulldata("@javascript")to call your functions from XLSForm calculations and constraints - Test and debug: Use the Scripts tab in Survey123 Connect to test functions and debug issues
- Publish and share: Publish your survey for organizational use and share with your team
JavaScript customization interface
JavaScript customization in Survey123 Connect provides a development environment for creating custom functions. You work with JavaScript files in the survey's scripts directory and integrate them with XLSForm expressions.
Key interface components:
- Scripts tab: Test and debug JavaScript functions in Survey123 Connect
- Scripts directory: File system location for JavaScript files in your survey project
- XLSForm integration: Use
pulldata("@javascript")to call functions from calculations and constraints - Console logging: Debug output and error messages in the Scripts tab
JavaScript file structure
JavaScript files must be placed in the scripts folder within your survey project directory:
your-survey-project/
├── survey.xlsx
├── scripts/
│ ├── validation.js
│ ├── calculations.js
│ └── transformation.js
└── media/JavaScript function capabilities
When creating JavaScript functions for Survey123, you can implement various capabilities:
Data processing:
- String manipulation and parsing
- Mathematical calculations and business logic
- Array and object handling
- Data validation and formatting
Integration features:
- Custom validation rules beyond XLSForm constraints
- Complex calculations with multiple inputs
- Data transformation for external system integration
- Reusable functions across multiple surveys
Function types:
- Validation functions (return validation messages)
- Calculation functions (return computed values)
- Transformation functions (format and parse data)
- Utility functions (helper functions for common operations)
Best practices
Follow these essential best practices to create effective JavaScript functions:
- Handle null values: Always check for null, undefined, or empty inputs
- Add error handling: Implement try-catch blocks and validation for robust functions
- Test thoroughly: Test functions with various inputs including edge cases and invalid data
- Test organization access: Ensure functions work for users within your ArcGIS organization
- Keep functions simple: Avoid complex logic that may impact performance
Handling repeat groups
JavaScript functions can work with repeat groups in two ways:
Pass a single question from a repeat:
pulldata("@javascript", "your
Pass all values from a repeat:
pulldata("@javascript", "your
When passing repeat data, the function receives a JSON object with individual questions as properties.
Code examples
Below are practical examples showing how to implement JavaScript functions for common Survey123 scenarios:
Basic string manipulation
Create a function to convert text to uppercase and handle null values safely.
// uppercase.js
function toUpperCase(input) {
if (input == null || input === '') return '';
return input.toString().toUpperCase();
}
function formatName(firstName, lastName) {
if (!firstName && !lastName) return '';
var first = firstName ? firstName.trim() : '';
var last = lastName ? lastName.trim() : '';
// Filter out empty strings and join with space to avoid leading/trailing spaces
var names = [first, last].filter(function(n) { return n; });
return names.join(' ');
}XLSForm usage:
| type | name | label | calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| text | first_name | First Name | |
| text | last_name | Last Name | |
| calculate | full_name | Full Name | pulldata("@javascript", "uppercase.js", "format |
| calculate | upper_name | Uppercase Name | pulldata("@javascript", "uppercase.js", "to |
Complex validation
Implement custom validation logic that checks multiple conditions.
// validation.js
function validateEmail(email) {
try {
if (!email) return 'Email is required';
var emailRegex = /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/;
if (!emailRegex.test(email)) {
return 'Please enter a valid email address';
}
return 'valid';
} catch (error) {
return 'Validation error occurred';
}
}
function validateAge(age, minAge, maxAge) {
try {
if (!age) return 'Age is required';
var numAge = parseInt(age);
if (isNaN(numAge)) return 'Age must be a number';
if (numAge < minAge || numAge > maxAge) {
return 'Age must be between ' + minAge + ' and ' + maxAge;
}
return 'valid';
} catch (error) {
return 'Validation error occurred';
}
}XLSForm usage:
| type | name | label | constraint | constraint_message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| text | Email Address | pulldata("@javascript", "validation.js", "validate | pulldata("@javascript", "validation.js", "validate | |
| integer | age | Age | pulldata("@javascript", "validation.js", "validate | pulldata("@javascript", "validation.js", "validate |
Advanced calculations
Perform complex mathematical operations for geospatial data processing.
// calculations.js
function calculateDistance(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2) {
// Calculate distance between two coordinates using Haversine formula (in meters)
if (!lat1 || !lon1 || !lat2 || !lon2) return null;
try {
var lat1Rad = parseFloat(lat1) * Math.PI / 180;
var lat2Rad = parseFloat(lat2) * Math.PI / 180;
var deltaLat = (parseFloat(lat2) - parseFloat(lat1)) * Math.PI / 180;
var deltaLon = (parseFloat(lon2) - parseFloat(lon1)) * Math.PI / 180;
var a = Math.sin(deltaLat / 2) * Math.sin(deltaLat / 2) +
Math.cos(lat1Rad) * Math.cos(lat2Rad) *
Math.sin(deltaLon / 2) * Math.sin(deltaLon / 2);
var c = 2 * Math.atan2(Math.sqrt(a), Math.sqrt(1 - a));
var earthRadius = 6371000; // Earth radius in meters
return Math.round(earthRadius * c * 10) / 10; // Round to 1 decimal place
} catch (error) {
return null;
}
}
function convertToDMS(decimal, isLatitude) {
// Convert decimal degrees to Degrees Minutes Seconds format
if (decimal == null || decimal === '') return '';
var absolute = Math.abs(parseFloat(decimal));
var degrees = Math.floor(absolute);
var minutesDecimal = (absolute - degrees) * 60;
var minutes = Math.floor(minutesDecimal);
var seconds = Math.round((minutesDecimal - minutes) * 60 * 100) / 100;
var direction = '';
if (isLatitude) {
direction = decimal >= 0 ? 'N' : 'S';
} else {
direction = decimal >= 0 ? 'E' : 'W';
}
return degrees + '° ' + minutes + "' " + seconds + '" ' + direction;
}
function calculateArea(length, width, unit) {
// Calculate area and convert units (supports meters and feet)
if (!length || !width) return null;
var lengthNum = parseFloat(length);
var widthNum = parseFloat(width);
if (lengthNum <= 0 || widthNum <= 0) return null;
var area = lengthNum * widthNum;
// Convert to acres or hectares based on unit
if (unit === 'feet') {
return Math.round(area / 43560 * 100) / 100; // Convert sq ft to acres
} else {
return Math.round(area / 10000 * 100) / 100; // Convert sq m to hectares
}
}XLSForm usage:
| type | name | label | calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| geopoint | start_location | Start Location | |
| geopoint | end_location | End Location | |
| calculate | distance | Distance (m) | pulldata("@javascript", "calculations.js", "calculate |
| decimal | sample_lat | Sample Latitude | |
| calculate | lat_dms | Latitude (DMS) | pulldata("@javascript", "calculations.js", "convert |
| decimal | sample_lon | Sample Longitude | |
| calculate | lon_dms | Longitude (DMS) | pulldata("@javascript", "calculations.js", "convert |
| decimal | plot_length | Plot Length (m) | |
| decimal | plot_width | Plot Width (m) | |
| calculate | plot_area | Plot Area (ha) | pulldata("@javascript", "calculations.js", "calculate |
Data transformation
Parse and format data for integration with other systems.
// transformation.js
function formatPhoneNumber(phone) {
if (!phone) return '';
// Remove all non-digit characters
var digits = phone.replace(/\D/g, '');
if (digits.length === 10) {
return '(' + digits.slice(0,3) + ') ' + digits.slice(3,6) + '-' + digits.slice(6);
} else if (digits.length === 11 && digits[0] === '1') {
return '+1 (' + digits.slice(1,4) + ') ' + digits.slice(4,7) + '-' + digits.slice(7);
}
return phone; // Return original if can't format
}
function parseAddressStreet(address) {
if (!address) return '';
var parts = address.split(',');
return parts[0] ? parts[0].trim() : '';
}
function parseAddressCity(address) {
if (!address) return '';
var parts = address.split(',');
return parts[1] ? parts[1].trim() : '';
}
function parseAddressState(address) {
if (!address) return '';
var parts = address.split(',');
return parts[2] ? parts[2].trim() : '';
}
function parseAddressZip(address) {
if (!address) return '';
var parts = address.split(',');
return parts[3] ? parts[3].trim() : '';
}
function formatCurrency(amount, currency) {
if (!amount || isNaN(amount)) return '';
currency = currency || 'USD';
var numAmount = parseFloat(amount);
// Simple currency formatting that works in all JavaScript environments
// Note: Intl.NumberFormat may not be available in Survey123's sandboxed environment
var formatted = numAmount.toFixed(2);
var symbol = currency === 'USD' ? '$' : currency + ' ';
return symbol + formatted.replace(/\B(?=(\d{3})+(?!\d))/g, ',');
}XLSForm usage:
| type | name | label | calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| text | phone | Phone Number | |
| calculate | formatted_phone | Formatted Phone | pulldata("@javascript", "transformation.js", "format |
| text | address | Full Address (format: street, city, state, zip) | |
| calculate | street | Street Address | pulldata("@javascript", "transformation.js", "parse |
| calculate | city | City | pulldata("@javascript", "transformation.js", "parse |
| calculate | state | State | pulldata("@javascript", "transformation.js", "parse |
| calculate | zip | ZIP Code | pulldata("@javascript", "transformation.js", "parse |
| decimal | amount | Amount | |
| calculate | formatted_amount | Formatted Amount | pulldata("@javascript", "transformation.js", "format |
Tutorials
Create a smarter, responsive survey
Learn how to create intelligent surveys with conditional logic, hidden fields, and dynamic visibility using ArcGIS Survey123 and XLSForm.
Low-code/no-code

Create a simple survey
Learn how to use ArcGIS Survey123 to create a simple survey.
Low-code/no-code
Analyze survey results
Learn how to use ArcGIS Survey123 to analyze survey results.
Low-code/no-code

Create a survey and dashboard for park maintenance
Learn how to integrate ArcGIS Survey123 with ArcGIS Dashboards to create a reporting solution.
Low-code/no-code