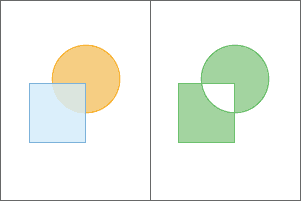
ST_SymDifference takes two geometry columns and returns a geometry column. The output column contains the
geometries that represent the portions of the input geometries that do not intersect. If one of the input geometry types is geometry, the output
type will be the same. For all other cases the result geometry type will be the same as the input geometry type with the
highest dimension.
| Function | Syntax |
|---|---|
| Python | sym |
| SQL | ST |
| Scala | sym |
For more details, go to the GeoAnalytics for Microsoft Fabric API reference for sym_difference.
This function implements the OpenGIS Simple Features Implementation Specification for SQL 1.2.1.
Python and SQL Examples
from geoanalytics_fabric.sql import functions as ST, Point, Polygon
df = spark.createDataFrame([(Point(8,8), Polygon([[[0,0],[10,0],[10,10],[0,10]]]),)], ["point", "polygon"])
df.select(ST.sym_difference(ST.buffer("point", 5), "polygon")).st.plot()
Scala Example
import com.esri.geoanalytics.geometry._
import com.esri.geoanalytics.sql.{functions => ST}
import org.apache.spark.sql.{functions => F}
case class GeometryRow(point: Point, polygon: Polygon)
val data = Seq(GeometryRow(Point(8, 8), Polygon(Point(0, 0), Point(0, 10), Point(10, 10), Point(10, 0))))
val df = spark.createDataFrame(data)
.select(ST.symDifference(ST.buffer($"point", 5), $"polygon").alias("sym_difference"))
.withColumn("difference_area", F.round(ST.area($"sym_difference"),3))
df.show()+--------------------+---------------+
| sym_difference|difference_area|
+--------------------+---------------+
|{"rings":[[[13,8]...| 92.35|
+--------------------+---------------+Version table
| Release | Notes |
|---|---|
1.0.0-beta | Python, SQL, and Scala functions introduced |