Perform a viewshed analysis from a defined vantage point.
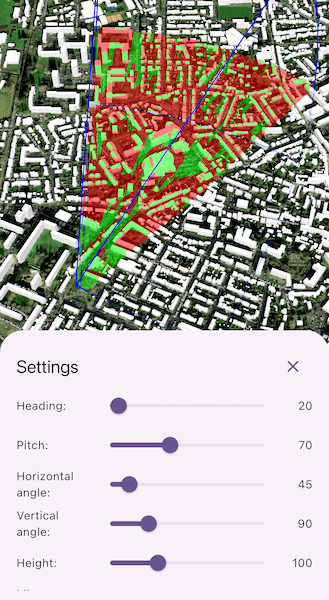
Use case
A 3D viewshed analysis is a type of visual analysis you can perform on a scene. The viewshed shows what can be seen from a given location. The output is an overlay with two different colors - one representing the visible areas (green) and the other representing the obstructed areas (red). Viewshed analysis is a form of "exploratory analysis", which means the results are calculated on the current scale of the data, and the results are generated very quickly. If more "conclusive" results are required, consider using a GeoprocessingTask to perform a viewshed instead.
How to use the sample
Tap a location on the map to change the location of the viewshed observation point.
Tap the "Settings" button at the bottom of the screen to show the controls to change the viewshed settings. The rendered viewshed will update in real time as the values are adjusted.
How it works
- Create a
LocationViewshedpassing in the observer location, heading, pitch, horizontal/vertical angles, and min/max distances. - Set the property values on the viewshed instance for location, direction, range, and visibility properties.
Relevant API
- AnalysisOverlay
- ArcGISSceneLayer
- ArcGISTiledElevationSource
- LocationViewshed
- Viewshed
About the data
The scene shows a buildings layer in Brest, France hosted on ArcGIS Online.
Tags
3D, frustum, scene, viewshed, visibility analysis
Sample Code
// Copyright 2025 Esri
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
//
import 'package:arcgis_maps/arcgis_maps.dart';
import 'package:arcgis_maps_sdk_flutter_samples/common/common.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class ShowViewshedFromPointInScene extends StatefulWidget {
const ShowViewshedFromPointInScene({super.key});
@override
State<ShowViewshedFromPointInScene> createState() =>
_ShowViewshedFromPointInSceneState();
}
class _ShowViewshedFromPointInSceneState
extends State<ShowViewshedFromPointInScene>
with SampleStateSupport {
// Create a controller for the scene view.
final _sceneViewController = ArcGISSceneView.createController();
// A flag indicating whether to show the settings bottom sheet.
bool _settingsVisible = false;
// Viewshed state variables.
double _heading = 20;
double _pitch = 70;
double _horizontalAngle = 45;
double _verticalAngle = 90;
double _height = 100;
double _minDistance = 5;
double _maxDistance = 1000;
bool _showFrustum = false;
bool _showAnalysis = true;
late final LocationViewshed _viewshed;
// A flag for when the scene view is ready and controls can be used.
var _ready = false;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
// Initialize the viewshed.
_viewshed = LocationViewshed.withLocation(
location: ArcGISPoint(
x: -4.50,
y: 48.4,
z: _height,
spatialReference: SpatialReference.wgs84,
),
heading: _heading,
pitch: _pitch,
horizontalAngle: _horizontalAngle,
verticalAngle: _verticalAngle,
minDistance: _minDistance,
maxDistance: _maxDistance,
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: SafeArea(
top: false,
left: false,
right: false,
child: Stack(
children: [
Column(
children: [
Expanded(
// Add a scene view to the widget tree and set a controller.
child: ArcGISSceneView(
controllerProvider: () => _sceneViewController,
onSceneViewReady: onSceneViewReady,
onTap: onTap,
),
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
// Button to show the viewshed options.
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => setState(() => _settingsVisible = true),
child: const Text('Settings'),
),
],
),
],
),
// Display a progress indicator and prevent interaction until state is ready.
LoadingIndicator(visible: !_ready),
],
),
),
bottomSheet: _settingsVisible ? buildSettings(context) : null,
);
}
Widget buildSettings(BuildContext context) {
// Create the BottomSheet containing the viewshed adjustment controls.
return BottomSheetSettings(
onCloseIconPressed: () => setState(() => _settingsVisible = false),
settingsWidgets: (context) => [
SizedBox(
height: 250,
child: SingleChildScrollView(
child: Column(
children: [
Table(
columnWidths: const <int, TableColumnWidth>{
0: FractionColumnWidth(0.25),
1: FlexColumnWidth(),
2: FixedColumnWidth(35),
},
defaultVerticalAlignment: TableCellVerticalAlignment.middle,
children: [
TableRow(
children: [
const Text('Heading:'),
Slider(
value: _heading,
max: 360,
label: _heading.round().toString(),
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.heading = value;
setState(() => _heading = value);
},
),
Text(
_heading.round().toString(),
textAlign: TextAlign.end,
),
],
),
TableRow(
children: [
const Text('Pitch:'),
Slider(
value: _pitch,
max: 180,
label: _pitch.round().toString(),
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.pitch = value;
setState(() => _pitch = value);
},
),
Text(
_pitch.round().toString(),
textAlign: TextAlign.end,
),
],
),
TableRow(
children: [
const Text('Horizontal angle:'),
Slider(
value: _horizontalAngle,
max: 360,
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.horizontalAngle = value;
setState(() => _horizontalAngle = value);
},
),
Text(
_horizontalAngle.round().toString(),
textAlign: TextAlign.end,
),
],
),
TableRow(
children: [
const Text('Vertical angle:'),
Slider(
value: _verticalAngle,
max: 360,
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.verticalAngle = value;
setState(() => _verticalAngle = value);
},
),
Text(
_verticalAngle.round().toString(),
textAlign: TextAlign.end,
),
],
),
TableRow(
children: [
const Text('Height:'),
Slider(
value: _height,
min: 10,
max: 300,
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.location = ArcGISPoint(
x: _viewshed.location.x,
y: _viewshed.location.y,
z: value,
spatialReference: SpatialReference.wgs84,
);
setState(() => _height = value);
},
),
Text(
_height.round().toString(),
textAlign: TextAlign.end,
),
],
),
TableRow(
children: [
const Text('Min distance:'),
Slider(
value: _minDistance,
max: 50,
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.minDistance = value;
setState(() => _minDistance = value);
},
),
Text(
_minDistance.round().toString(),
textAlign: TextAlign.end,
),
],
),
TableRow(
children: [
const Text('Max distance:'),
Slider(
value: _maxDistance,
min: 100,
max: 5000,
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.maxDistance = value;
setState(() => _maxDistance = value);
},
),
Text(
_maxDistance.round().toString(),
textAlign: TextAlign.end,
),
],
),
],
),
Row(
children: [
const Text('Show frustum:'),
const Spacer(),
Switch(
value: _showFrustum,
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.frustumOutlineVisible = value;
setState(() => _showFrustum = value);
},
),
],
),
Row(
children: [
const Text('Show viewshed:'),
const Spacer(),
Switch(
value: _showAnalysis,
onChanged: (value) {
_viewshed.isVisible = value;
setState(() => _showAnalysis = value);
},
),
],
),
],
),
),
),
],
);
}
void onSceneViewReady() {
// Get scene with basemap, surface, and initial viewpoint.
final scene = _setupScene();
// Add a buildings scene layer.
final buildingLayerUri = Uri.parse(
'https://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P3ePLMYs2RVChkJx/arcgis/rest/services/Buildings_Brest/SceneServer/layers/0',
);
final buildingsLayer = ArcGISSceneLayer.withUri(buildingLayerUri);
scene.operationalLayers.add(buildingsLayer);
// Add the scene to the view controller.
_sceneViewController.arcGISScene = scene;
// Create an AnalysisOverlay and add the viewshed.
final analysisOverlay = AnalysisOverlay();
analysisOverlay.analyses.add(_viewshed);
// Add the AnalysisOverlay to the view controller.
_sceneViewController.analysisOverlays.add(analysisOverlay);
// Set the ready state variable to true to enable the sample UI.
setState(() => _ready = true);
}
void onTap(Offset offset) {
final tapLocation = _sceneViewController.screenToBaseSurface(
screen: offset,
);
if (tapLocation == null) return;
// Set the new viewshed location using the x and y values from the tap point
// and the current viewshed height.
_viewshed.location = ArcGISPoint(
x: tapLocation.x,
y: tapLocation.y,
z: _height,
spatialReference: SpatialReference.wgs84,
);
}
ArcGISScene _setupScene() {
// Create a scene with an imagery basemap style.
final scene = ArcGISScene.withBasemapStyle(BasemapStyle.arcGISImagery);
// Setup the initial viewpoint for the scene.
final camera = Camera.withLookAtPoint(
lookAtPoint: ArcGISPoint(
x: -4.50,
y: 48.4,
z: 100,
spatialReference: SpatialReference.wgs84,
),
distance: 200,
heading: 20,
pitch: 70,
roll: 0,
);
scene.initialViewpoint = Viewpoint.withExtentCamera(
targetExtent: camera.location,
camera: camera,
);
// Add surface elevation to the scene.
final worldElevationService = Uri.parse(
'https://elevation3d.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/WorldElevation3D/Terrain3D/ImageServer',
);
final elevationSource = ArcGISTiledElevationSource.withUri(
worldElevationService,
);
scene.baseSurface.elevationSources.add(elevationSource);
return scene;
}
}