Migration
The steps required to migrate to ArcGIS depend on the type of application you have, how the map and data are styled, and what additional mapping functionality is supported. In most cases, the map style can be replaced with styles from the ArcGIS Basemap Styles service, data can be hosted with data services, and mapping functionality such as geocoding and routing can be replaced with location services.
Learn more about the steps to migrate below.
Steps
- Library migration: Update apps to use the MapLibre GL JS library.
- Map migration: Display basemap styles with the MapLibre ArcGIS plugin.
- Data migration: Manage your map data with hosted data services and display data with the MapLibre ArcGIS plugin.
- Location services migration: Add additional mapping functionality with ArcGIS REST JS and location services.
1. Library migration
The first step to migrate Mapbox GL JS applications is to update your code to use the MapLibre GL JS library. MapLibre GL JS is officially supported for building applications with ArcGIS services. Updating will also allow you to use the MapLibre ArcGIS plugin to easily access basemap styles and display data in your maps.
Mapbox to MapLibre
In most cases, you can simply replace Mapbox libraries with MapLibre library references. MapLibre GL JS is backwards compatible with Mapbox GL JS (version 1). For more information, go to the MapLibre GL JS > Mapbox migration guide.
How to update libraries
<script src="https://api.tiles.mapbox.com/mapbox-gl-js/vx.x.x/mapbox-gl.js"></script>
<link href="https://api.tiles.mapbox.com/mapbox-gl-js/vx.x.x/mapbox-gl.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src=https://unpkg.com/maplibre-gl@5.19.0/dist/maplibre-gl.js></script>
<link href=https://unpkg.com/maplibre-gl@5.19.0/dist/maplibre-gl.css rel="stylesheet" />2. Map migration
In Mapbox, you display a map by referencing a style. A style defines the visual appearance of a map and includes the required data sources and styling rules. In ArcGIS, you display a map by referencing a basemap style. You can use default basemap styles or create your own custom style.
Steps
- Select a basemap style with the Style Explorer or create a custom style.
- Use the MapLibre ArcGIS plugin to display the basemap style.
Mapbox and ArcGIS styles
Use the table below to match styles and view the styles in the Style Explorer.
| Mapbox styles | ArcGIS Basemap styles | ArcGIS Open Basemap styles |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Day | arcgis/navigation (with POIs enabled)arcgis/streets (with POIs enabled) | open/streets |
| Standard Monochrome | arcgis/light-gray | open/light-gray |
| Standard Dark | arcgis/navigation-night (with POIs enabled)arcgis/streets-night (with POIs enabled) | open/streets-nightopen/navigation-dark |
| Standard Satellite | arcgis/imagery (with POIs enabled) | open/hybrid |
| Street* | arcgis/streets | open/streetsopen/osm-style |
| Navigation Day* | arcgis/navigation | open/navigation |
| Navigation Night* | arcgis/navigation-night | open/navigation-darkopen/streets-night |
| Satellite* | arcgis/imageryarcgis/imagery-standard | open/hybrid |
| Light* | arcgis/light-gray | open/light-gray |
| Dark* | arcgis/dark-gray | open/dark-gray |
| Outdoors* | arcgis/outdoorarcgis/topographicarcgis/terrain | open/osm-style-relief |
* Legacy Mapbox classic styles
Style Explorer
Basemap styles
To update an application to use an ArcGIS basemap style, you need to select a style from the Basemap Styles service. The service supports both ArcGIS styles and Open styles.
Custom basemap styles
To create a custom basemap style for your map, you can use the ArcGIS Vector Tile Style Editor. The ArcGIS Vector Tile Style Editor allows you to select an existing style, edit, and save it as a new style. The new style is saved in your portal as new as vector tile layer item. The item has a unique item ID that you can use to display the new style in your application.
3. Data migration
In Mapbox, you display data by adding additional data sources and layers to a map. A data source provides data in a supported format such as GeoJSON features or vector tiles. In ArcGIS, you can create data sources for mapping applications by hosting your data with data services. To do so, you use ArcGIS portal to import your data and create feature services, vector tile services, or map tile services. After creating services, you can display the data by adding new data sources to your map.
Steps
- Use ArcGIS portal to import and host your data as feature data or vector tile data.
- Style the data on the client or server.
- Use the MapLibre ArcGIS plugin to access and display the hosted data.
Feature data
To host your feature data, use the ArcGIS portal to import your data to create a feature service. You can import different file formats such as CSV, GeoJSON, and Shapefiles. Feature services support SQL and spatial queries, which means you don’t have to load the entire dataset and only display a set of GeoJSON features in an application. The features are typically styled in the client application.
Vector tile data
To host your data as vector tiles, use the ArcGIS portal to import feature data and then publish it as a vector tile service. This is typically used for applications that need to display large or complex geographic datasets. You can pre-style the features beforehand and/or post-style the vector tiles afterwards with the ArcGIS Vector Tile Style Editor. The vector tiles can be styled and displayed in the client application.
4. Location services migration
To migrate or add additional mapping functionality to a MapLibre GL JS application, use the ArcGIS REST JS library to access ArcGIS services. The library can access ArcGIS Location Services, data services, or the spatial analysis service.
Steps
- Select a service to perform geocoding, routing, place finding, elevation finding, data enrichment, or spatial analysis.
- Access the service with ArcGIS REST JS.
- Display the map and data with the MapLibre ArcGIS plugin.
Geocoding
Use ArcGIS REST JS and the ArcGIS Geocoding service to perform address matching, reverse geocoding, and address suggestions.
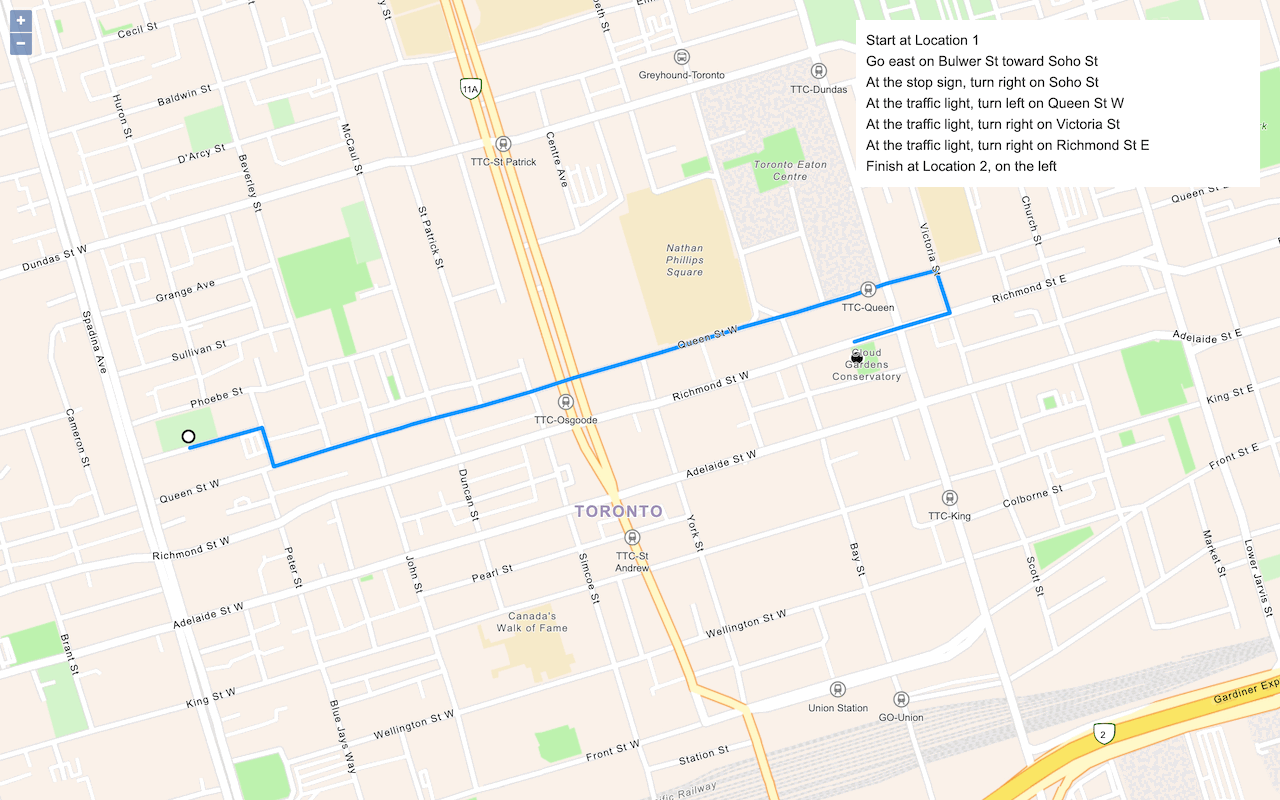
Routing
Use ArcGIS REST JS and the ArcGIS Routing service to find routes and directions and get service areas.
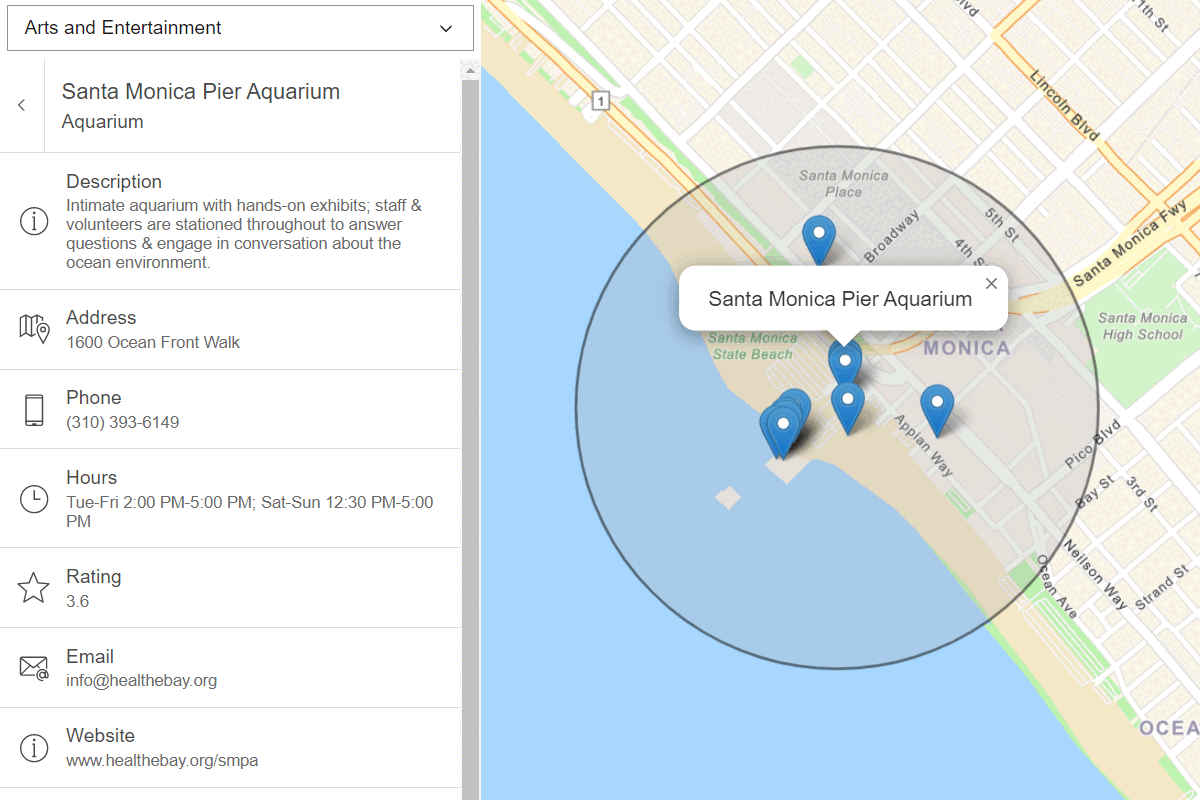
Places
Use ArcGIS REST JS and the ArcGIS Places service to find places by categories and get place details.
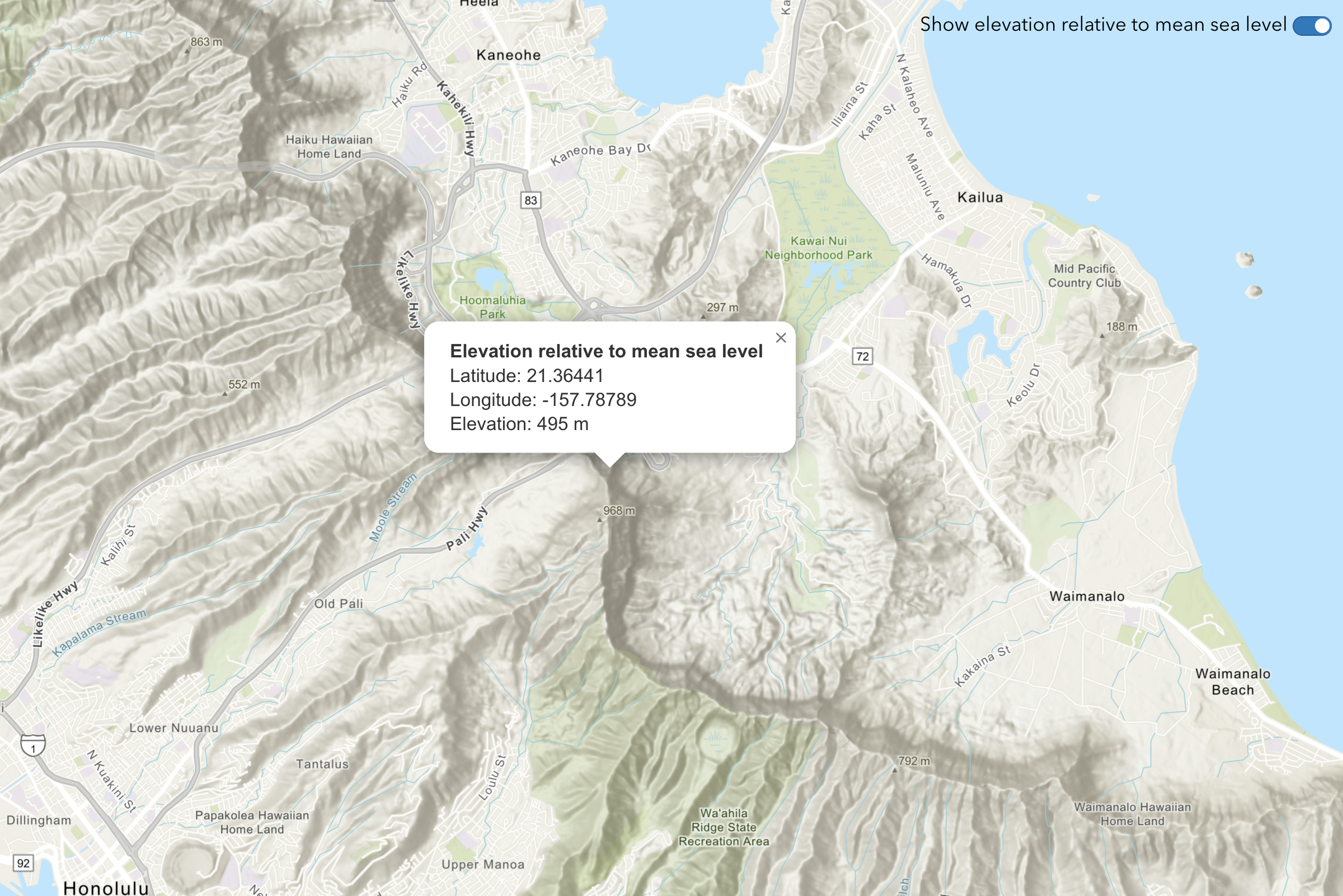
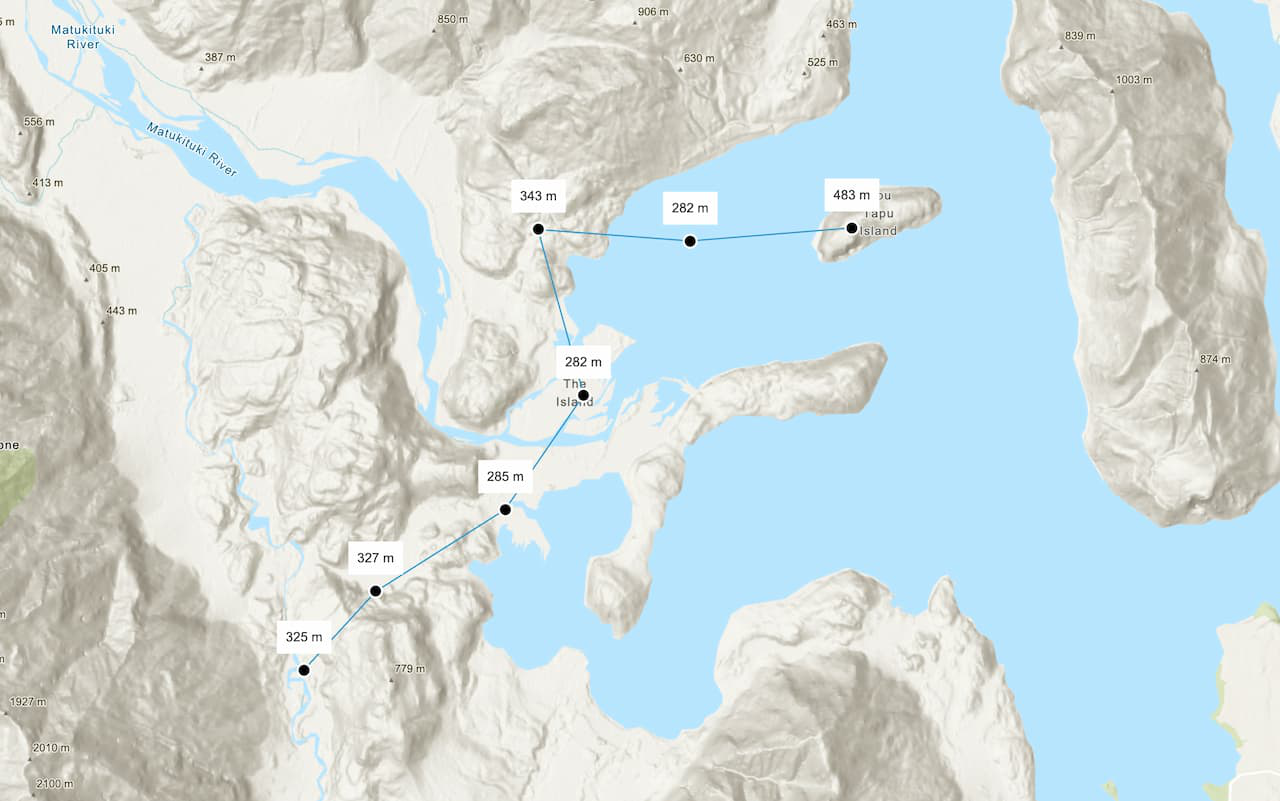
Elevation
Use ArcGIS REST JS and the ArcGIS Elevation service to find topobathy elevation values for locations.
GeoEnrichment
Use ArcGIS REST JS and the ArcGIS GeoEnrichment service to find demographic information and local facts for areas.