The ArcGIS Location component is used to place game objects at specific geographical coordinates. This component is integrated with Unity's high precision framework and gives the game object the ability to transform its location to geographic coordinates. For example, you can use the ArcGIS Location component to place a 3D model of the Eiffel Tower with an accurate geographic position and rotation.

High Precision Framework
ArcGIS Maps SDK for Unity has native geospatial placement that uses the high-precision framework, which was developed by Unity and integrated within the ArcGIS Maps SDK for Unity. The high-precision framework, allows Unity to render very large worlds and addresses many of the limitations of working with 32-bit floating point precision.
When you create an ArcGIS Map, the HPRoot component will be automatically added to set the Origin position. The HPTranform component must be a child of HPRoot and works together with the ArcGIS Location component to convert double precision to 32-bit floating point precision. In a scene that uses the high-precision framework, HPTranform should be used instead of Transform. A game object with an HPTransform cannot be a child of another HPTransform.
Use the ArcGIS Location component
To position your project's existing game objects in real world locations, you can add an ArcGIS Location component. You can search for it in the project folder.
If you are going to develop an app with the C# API, make sure game objects with the ArcGIS Location component are children of the game object that contains the ArcGIS MapView component.
If you select the Map Creator UI or components development option in order to use an ArcGIS Location component:
-
Click the game object in the Hierarchy window and click Add Component to select the ArcGIS Location component to add the script. For more information about components, see Unity's documentation: Use components.
-
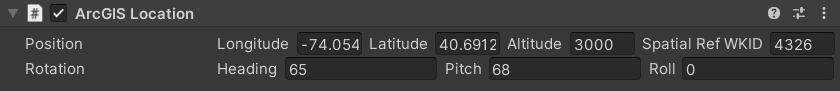
Select the game object and set the initial position and rotation of the game object in the Inspector.
- X (Longitude) : Specifies the east–west position of the Actor on the Earth's surface. A projected position value for projected coordinate systems or a longitude value for geographic coordinate systems.
- Y (Latitude) : Specifies the north–south position of the Actor on the Earth's surface. A projected position value for projected coordinate systems or a latitude value for geographic coordinate systems.
- Z (Altitude): Sets the vertical distance of the Actor above the Earth. The units depend on the spatial reference.
- Spatial Reference WKID: Well-known ID (WKID) of the spatial reference for the X, Y and Z values. (Specifying the spatial reference with Well-Known Text (WKT) is not supported for the ArcGIS Location Component.)
- Heading: Sets the heading or up axis of the Actor. This is also known as yaw or azimuth. It represents the number of degrees by which the game object will be rotated, measured counterclockwise from the north. To rotate clockwise, use a negative value.
- Pitch: Sets the pitch or right axis of the Actor. Pitch is the equivalent of moving a plane's nose up or down (rotating along the axis that passes through the plane's wings). Positive values, looking forward, are above the horizon (pointing upward) and negative values are below the horizon (pointing downward).
- Roll: Sets the roll or forward axis of the Actor. Roll is the equivalent of tilting a plane's wings up or down (rotating along the axis that passes through the center of the plane from front to back). A zero value is perfectly horizontal. Positive values will tilt the left side upward (or right side downward). Negative values do the opposite.