Calculate a geodesic path between two points and measure its distance.
Use case
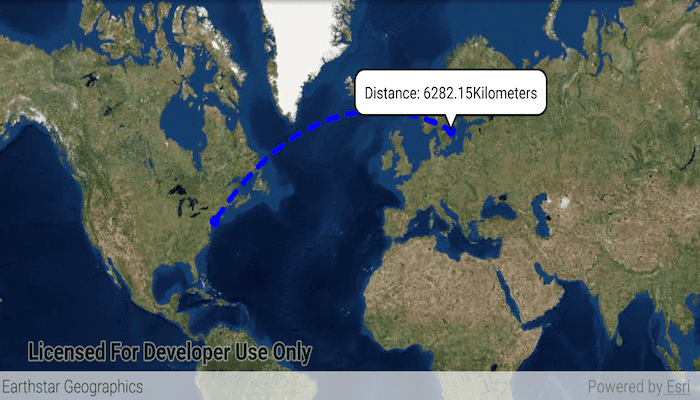
A geodesic distance provides an accurate, real-world distance between two points. Visualizing flight paths between cities is a common example of a geodesic operation since the flight path between two airports takes into account the curvature of the earth, rather than following the planar path between those points, which appears as a straight line on a projected map.
How to use the sample
Tap anywhere on the map. A line graphic will display the geodesic line between the two points. In addition, text that indicates the geodesic distance between the two points will be updated. Tap elsewhere and a new line will be created.
How it works
- Create a
Pointand display it as aGraphic. - Obtain a new point when a tap occurs on the
MapViewand add this point as a graphic. - Create a
Polylinefrom the two points. - Execute
GeometryEngine.densifyGeodeticby passing in the created polyine then create a graphic from the returnedGeometry. - Execute
GeometryEngine.lengthGeodeticby passing in the two points and display the returned length on the screen.
Relevant API
- GeometryEngine.densifyGeodetic
- GeometryEngine.lengthGeodetic
About the data
The Imagery basemap provides the global context for the displayed geodesic line.
Tags
densify, distance, geodesic, geodetic
Sample Code
/* Copyright 2018 Esri
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
*/
package com.esri.arcgisruntime.geodesicoperations;
import java.util.Arrays;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.ArcGISRuntimeEnvironment;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.GeodeticCurveType;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.Geometry;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.GeometryEngine;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.LinearUnit;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.LinearUnitId;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.Point;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.PointCollection;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.Polyline;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.SpatialReferences;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.ArcGISMap;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.BasemapStyle;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.Callout;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.DefaultMapViewOnTouchListener;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.Graphic;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.GraphicsOverlay;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.MapView;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.symbology.SimpleLineSymbol;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.symbology.SimpleMarkerSymbol;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private MapView mMapView;
private final LinearUnit mUnitOfMeasurement = new LinearUnit(LinearUnitId.KILOMETERS);
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// authentication with an API key or named user is required to access basemaps and other
// location services
ArcGISRuntimeEnvironment.setApiKey(BuildConfig.API_KEY);
// create a map
ArcGISMap map = new ArcGISMap(BasemapStyle.ARCGIS_IMAGERY);
// set map to a map view
mMapView = findViewById(R.id.mapView);
mMapView.setMap(map);
// create a graphic overlay
GraphicsOverlay graphicsOverlay = new GraphicsOverlay();
mMapView.getGraphicsOverlays().add(graphicsOverlay);
// add a graphic at JFK to represent the flight start location
final Point start = new Point(-73.7781, 40.6413, SpatialReferences.getWgs84());
SimpleMarkerSymbol locationMarker = new SimpleMarkerSymbol(SimpleMarkerSymbol.Style.CIRCLE, Color.BLUE, 10);
Graphic startLocation = new Graphic(start, locationMarker);
graphicsOverlay.getGraphics().add(startLocation);
// create graphic for the destination
final Graphic endLocation = new Graphic();
endLocation.setSymbol(locationMarker);
graphicsOverlay.getGraphics().add(endLocation);
// create graphic representing the geodesic path between the two locations
final Graphic path = new Graphic();
path.setSymbol(new SimpleLineSymbol(SimpleLineSymbol.Style.DASH, Color.BLUE, 5));
graphicsOverlay.getGraphics().add(path);
// add onTouchListener to get the location of the user tap
mMapView.setOnTouchListener(new DefaultMapViewOnTouchListener(this, mMapView) {
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent motionEvent) {
// get the point that was clicked and convert it to a point in the map
android.graphics.Point clickLocation = new android.graphics.Point(Math.round(motionEvent.getX()),
Math.round(motionEvent.getY()));
Point mapPoint = mMapView.screenToLocation(clickLocation);
final Point destination = (Point) GeometryEngine.project(mapPoint, SpatialReferences.getWgs84());
endLocation.setGeometry(destination);
// create a straight line path between the start and end locations
PointCollection points = new PointCollection(Arrays.asList(start, destination), SpatialReferences.getWgs84());
Polyline polyline = new Polyline(points);
// densify the path as a geodesic curve and show it with the path graphic
Geometry pathGeometry = GeometryEngine
.densifyGeodetic(polyline, 1, mUnitOfMeasurement, GeodeticCurveType.GEODESIC);
path.setGeometry(pathGeometry);
// calculate the path distance
double distance = GeometryEngine.lengthGeodetic(pathGeometry, mUnitOfMeasurement, GeodeticCurveType.GEODESIC);
// create a textview for the callout
TextView calloutContent = new TextView(getApplicationContext());
calloutContent.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
calloutContent.setSingleLine();
// format coordinates to 2 decimal places
calloutContent.setText("Distance: " + String.format("%.2f", distance) + " Kilometers");
final Callout callout = mMapView.getCallout();
callout.setLocation(mapPoint);
callout.setContent(calloutContent);
callout.show();
return true;
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
mMapView.pause();
super.onPause();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mMapView.resume();
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
mMapView.dispose();
}
}