Display nautical charts per the ENC specification.
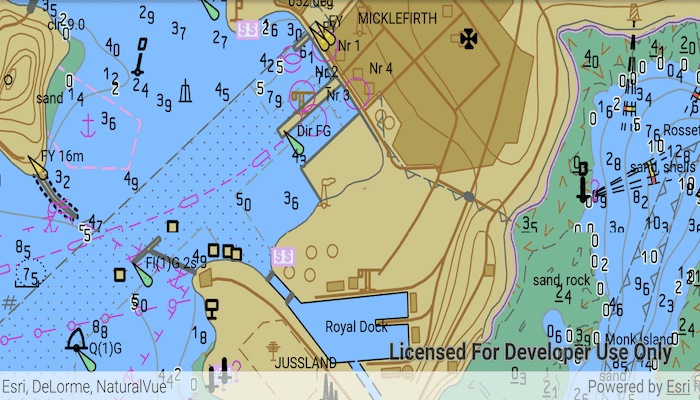
Use case
The ENC specification describes how hydrographic data should be displayed digitally.
An ENC exchange set is a catalog of data files which can be loaded as cells. The cells contain information on how symbols should be displayed in relation to one another, so as to represent information such as depth and obstacles accurately.
How to use the sample
Run the sample and view the ENC data. Pan and zoom around the map. Take note of the high level of detail in the data and the smooth rendering of the layer.
How it works
- Specify the path to a local CATALOG.031 file to create an
EncExchangeSet. - After loading the exchange set, get the
EncDatasetobjects in the exchange set withgetDatasets(). - Create an
EncCellfor each dataset. Then create anEncLayerfor each cell. - Add the ENC layer to a map's operational layers collection to display it.
Relevant API
- EncCell
- EncDataset
- EncExchangeSet
- EncLayer
Offline Data
- To use ENC in ArcGIS Runtime, extra resources are required. Download the data Hydrography Data supplement from ArcGIS for Developers and ENC Exchange Set without updates from ArcGIS Online.
- Extract the contents of the downloaded zip file to disk.
- Open your command prompt and navigate to the folder where you extracted the contents of the data from step 2.
- Push the data into the scoped storage of the sample app:
adb push hydrography /Android/data/com.esri.arcgisruntime.sample.addencexchangeset/files/hydrographyadb push ExchangeSetwithoutUpdates /Android/data/com.esri.arcgisruntime.sample.addencexchangeset/files/ExchangeSetwithoutUpdates
Tags
data, ENC, hydrographic, layers, maritime, nautical chart
Sample Code
MainActivity.java
/*
* Copyright 2019 Esri
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
*/
package com.esri.arcgisruntime.sample.addencexchangeset;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.ArcGISRuntimeEnvironment;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.Envelope;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.GeometryEngine;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.hydrography.EncCell;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.hydrography.EncDataset;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.hydrography.EncEnvironmentSettings;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.hydrography.EncExchangeSet;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.layers.EncLayer;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.loadable.LoadStatus;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.ArcGISMap;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.BasemapStyle;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.Viewpoint;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.MapView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
private MapView mMapView;
private Envelope mCompleteExtent;
// objects that implement Loadable must be class fields to prevent being garbage collected before loading
private EncExchangeSet mEncExchangeSet;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// authentication with an API key or named user is required to access basemaps and other
// location services
ArcGISRuntimeEnvironment.setApiKey(BuildConfig.API_KEY);
// get a reference to the map view
mMapView = findViewById(R.id.mapView);
// create a map with the Basemap Style topographic
ArcGISMap map = new ArcGISMap(BasemapStyle.ARCGIS_OCEANS);
// set the map to be displayed in this view
mMapView.setMap(map);
// set paths using ENC environment settings
// point to the folder containing hydrography resources
EncEnvironmentSettings
.setResourcePath(getExternalFilesDir(null) + getString(R.string.hydrography_directory));
// use the app's cache to store processed System Electronic Navigational Chart (SENC) data
EncEnvironmentSettings.setSencDataPath(getExternalCacheDir().getPath());
// create the Exchange Set passing an array of paths. Update sets can be loaded alongside base data
mEncExchangeSet = new EncExchangeSet(
Collections.singleton(getExternalFilesDir(null) + getString(R.string.enc_path)));
mEncExchangeSet.loadAsync();
mEncExchangeSet.addDoneLoadingListener(() -> {
if (mEncExchangeSet.getLoadStatus() == LoadStatus.LOADED) {
// add each data set's Enc cell as an ENC layer
for (EncDataset encDataset : mEncExchangeSet.getDatasets()) {
// create an ENC layer with an ENC cell using the dataset
EncLayer encLayer = new EncLayer(new EncCell(encDataset));
// add the ENC layer to the map's operational layers
mMapView.getMap().getOperationalLayers().add(encLayer);
encLayer.addDoneLoadingListener(() -> {
if (encLayer.getLoadStatus() == LoadStatus.LOADED) {
Envelope extent = encLayer.getFullExtent();
// combine extents of each layer
if (mCompleteExtent == null) {
mCompleteExtent = extent;
} else {
mCompleteExtent = GeometryEngine.combineExtents(Arrays.asList(mCompleteExtent, extent));
}
// set the view point to the extent of all enc layers
mMapView.setViewpointAsync(new Viewpoint(mCompleteExtent));
} else {
String error = "Error loading ENC layer: " + encLayer.getLoadError().getMessage();
Toast.makeText(this, error, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Log.e(TAG, error);
}
});
}
} else {
String error = "Error loading ENC exchange set: " + mEncExchangeSet.getLoadError().getMessage();
Toast.makeText(this, error, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Log.e(TAG, error);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
mMapView.pause();
super.onPause();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mMapView.resume();
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
mMapView.dispose();
super.onDestroy();
}
}