Add rasters and feature tables from a GeoPackage to a map.
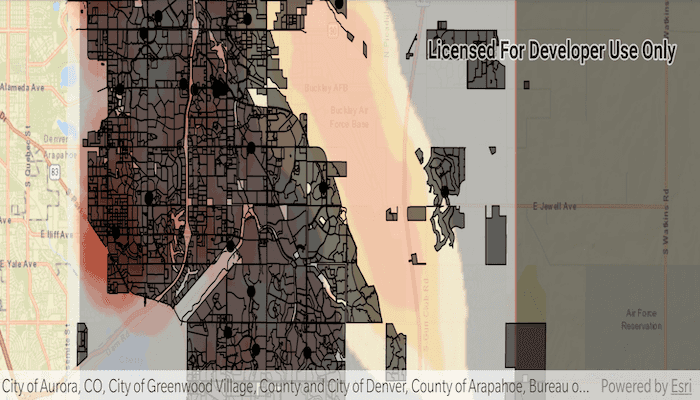
Use case
The OGC GeoPackage specification defines an open standard for sharing raster and vector data. You may want to use GeoPackage files to support file-based sharing of geographic data.
How to use the sample
When the sample loads, the feature tables and rasters from the GeoPackage are shown on the map.
How it works
- Open the
GeoPackagewith a path and load it usinggeoPackage.loadAsync(). - Iterate through available rasters, exposed by
geopackage.getGeoPackageRasters().- For each raster, create a new
Rasterlayer(geopackageRaster), then add it to the map.
- For each raster, create a new
- Iterate through available feature tables, exposed by
geopackage.getGeoPackageFeatureTables().- For each feature table, create a new
FeatureLayer(geopackageFeatureTable), then add it to the map.
- For each feature table, create a new
Relevant API
- GeoPackage
- GeoPackageFeatureTable
- GeoPackageRasters
Offline Data
- Download the data from ArcGIS Online.
- Extract the contents of the downloaded zip file to disk.
- Open your command prompt and navigate to the folder where you extracted the contents of the data from step 1.
- Push the data into the scoped storage of the sample app:
adb push AuroraCO.gpkg /Android/data/com.esri.arcgisruntime.sample.readgeopackage/files/AuroraCO.gpkg
About the data
This sample features a GeoPackage with datasets that cover Aurora, Colorado: Public art (points), Bike trails (lines), Subdivisions (polygons), Airport noise (raster), and liquour license density (raster).
Additional information
GeoPackage uses a single SQLite file (.gpkg) that conforms to the OGC GeoPackage Standard. You can create a GeoPackage file (.gpkg) from your own data using the create a SQLite Database tool in ArcGIS Pro.
Tags
container, layer, map, OGC, package, raster, table
Sample Code
/*
* Copyright 2018 Esri
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
*/
package com.esri.arcgisruntime.sample.readgeopackage;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.ArcGISRuntimeEnvironment;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.data.GeoPackage;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.data.GeoPackageFeatureTable;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.layers.FeatureLayer;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.layers.RasterLayer;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.loadable.LoadStatus;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.ArcGISMap;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.BasemapStyle;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.Viewpoint;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.MapView;
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.raster.GeoPackageRaster;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private final static String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
private MapView mMapView;
// objects that implement Loadable must be class fields to prevent being garbage collected before loading
private GeoPackage mGeoPackage;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// authentication with an API key or named user is required to access basemaps and other
// location services
ArcGISRuntimeEnvironment.setApiKey(BuildConfig.API_KEY);
// inflate MapView from layout
mMapView = findViewById(R.id.mapView);
// create a new map centered on Aurora Colorado and add it to the map view
ArcGISMap map = new ArcGISMap(BasemapStyle.ARCGIS_STREETS);
mMapView.setMap(map);
mMapView.setViewpoint(new Viewpoint( 39.7294, -104.8319, 1000000));
// open and load the GeoPackage
mGeoPackage = new GeoPackage(getExternalFilesDir(null) + getString(R.string.geopackage_path));
mGeoPackage.loadAsync();
mGeoPackage.addDoneLoadingListener(() -> {
if (mGeoPackage.getLoadStatus() == LoadStatus.FAILED_TO_LOAD) {
String error = "Geopackage failed to load: " + mGeoPackage.getLoadError();
Log.e(TAG, error);
Toast.makeText(this, error, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return;
}
// loop through each GeoPackageRaster
for (GeoPackageRaster geoPackageRaster : mGeoPackage.getGeoPackageRasters()) {
// create a RasterLayer from the GeoPackageRaster
RasterLayer rasterLayer = new RasterLayer(geoPackageRaster);
// set the opacity on the RasterLayer to partially visible
rasterLayer.setOpacity(0.55f);
// add the layer to the map
mMapView.getMap().getOperationalLayers().add(rasterLayer);
}
// loop through each GeoPackageFeatureTable
for (GeoPackageFeatureTable geoPackageFeatureTable : mGeoPackage.getGeoPackageFeatureTables()) {
// create a FeatureLayer from the GeoPackageFeatureLayer
FeatureLayer featureLayer = new FeatureLayer(geoPackageFeatureTable);
// add the layer to the map
mMapView.getMap().getOperationalLayers().add(featureLayer);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
mMapView.pause();
super.onPause();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mMapView.resume();
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
mMapView.dispose();
super.onDestroy();
}
}