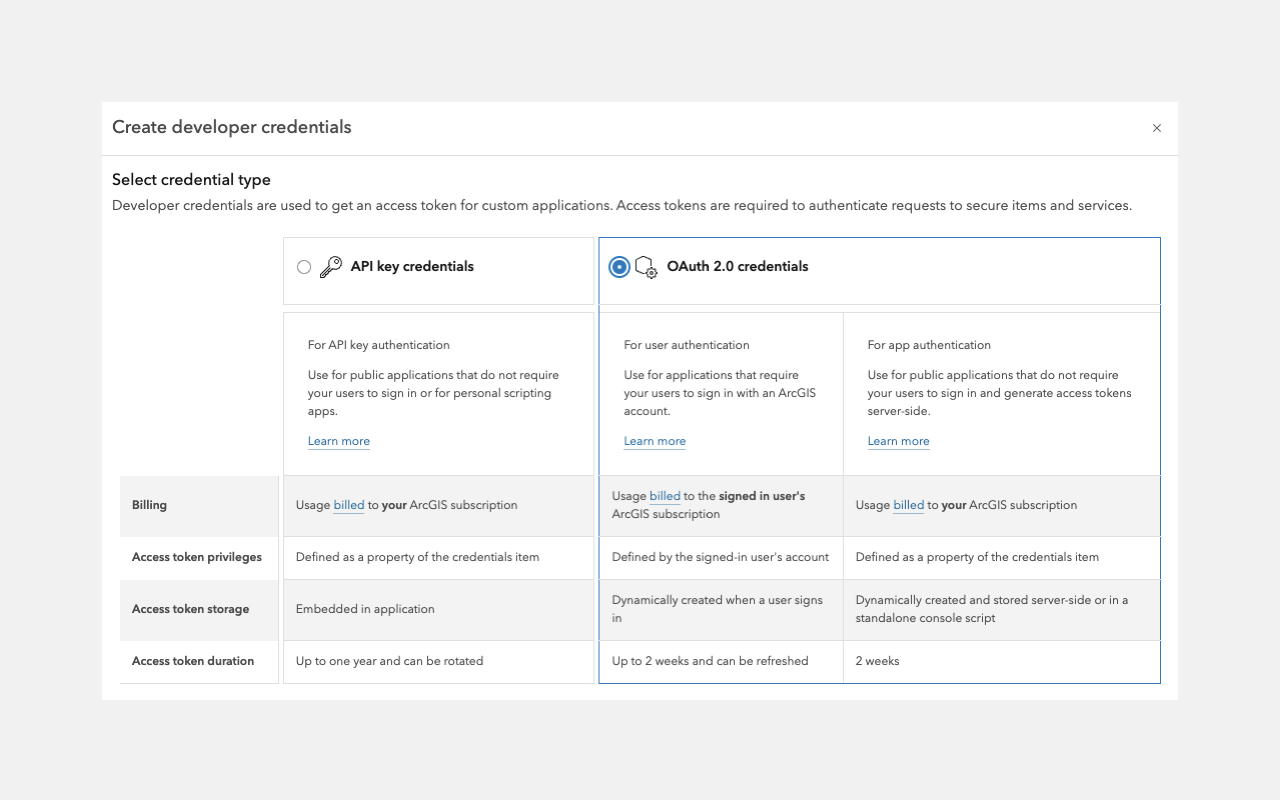
To build applications that use ArcGIS resources and services, you must first implement authentication to obtain an access token. There are two primary authentication methods: API key authentication and User authentication. The method you choose depends on several factors, including:
- The ArcGIS product you are using
- The type of application you're developing
- The types of resources and services you need to access
- The types of operations your application will perform
API keys
If you have ArcGIS Location Platform or ArcGIS Online, you can use API key authentication to authorize secure service requests without requiring users to sign in. This method requires creating an API key credential and embedding a long-lived access token directly in your application, granting access to specific services and content based on the API key’s configured privileges.
API keys can be configured to access specific ArcGIS services and functionality, including location services (such as basemaps, geocoding, and routing), hosted data services, and spatial analysis services. However, they do not support operations that require ArcGIS user account permissions, such as portal administration or content management. See user authentication for those scenarios.
API key authentication is well-suited for building public-facing applications that do not require user sign-in.
- Create an API key credential item in your portal.
- Assign privileges (scopes) to define accessible services and data.
- Use the access token to access services.
For step-by-step instructions, go to the tutorial below.
User tokens
If you have ArcGIS Online, you can build applications that authenticate users with their ArcGIS account. This process involves creating an OAuth credential, which is used to generate a unique access token tied to the user's privileges. With this token, applications can access all services and resources available to the signed-in user, including location services, spatial analysis, hosted data, secure items, and portal operations such as administration. Access is determined by the user's role and permissions.
User authentication is well-suited for building private applications for your organization that require users to sign in.
- Create an OAuth credential item in your portal to obtain a client ID, client secret, and redirect URL.
- Use these credentials in your application to initiate the OAuth 2.0 flow and request an access token.
- Use the access token to access services on behalf of the signed-in user.
For step-by-step instructions, go to the tutorial below.