ST_GeodesicBuffer takes a geometry column and a numeric distance value and returns a polygon column. The resulting buffer polygons represent the geodesic area that is less than or equal to the specified distance from each input geometry. The result will be in meters.
The distance can be specified with or without a unit.
When specified with a unit, the distance can be defined using ST_CreateDistance
or with a tuple containing a number and a unit string (e.g., (10, "kilometers")).
This function is more accurate but less performant than ST_Buffer and requires that a spatial reference is set on the input geometry column. To learn more about the difference between planar and geodesic calculations see Coordinate systems and transformations.
| Function | Syntax |
|---|---|
| Python | geodesic |
| SQL | ST |
| Python | geodesic |
For more details, go to the GeoAnalytics Engine API reference for geodesic_buffer.
This function implements the OpenGIS Simple Features Implementation Specification for SQL 1.2.1.
Python and SQL examples
from geoanalytics.sql import functions as ST
data = [
("POINT (-2533858.73 8107527.81)",),
("MULTIPOINT (-3159938.72 8190159.75, -3046133.91 8190159.75, -3188072.29 8103229.92)", ),
("LINESTRING (-3636954.77 7750916.26, -3168756.90 7966747.98, -3124795.45 7893415.62)", ),
("POLYGON ((-2299937.47 8474247.90, -2543511.83 8425946.52, -2488034.02 8322274.98, -2299937.47 8474247.90))", )
]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["wkt"])\
.select(ST.geom_from_text("wkt", srid=54008).alias("geometry"))
df = df.withColumn("geodesic_buffer", ST.geodesic_buffer("geometry", 60000))
ax = df.st.plot("geometry", facecolor="none", edgecolor="red")
ax.set_xticklabels(ax.get_xticklabels(),rotation=45)
df.st.plot("geodesic_buffer", ax=ax, facecolor="none", edgecolor="blue")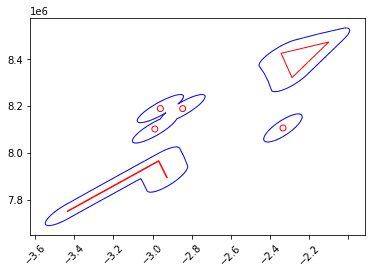
Scala examples
import com.esri.geoanalytics.sql.{functions => ST}
import org.apache.spark.sql.{functions => F}
case class GeometryRow(wkt: String)
val data = Seq(GeometryRow("POINT (-2533858.73 8107527.81)"),
GeometryRow("MULTIPOINT (-3159938.72 8190159.75, -3046133.91 8190159.75, -3188072.29 8103229.92)"),
GeometryRow("LINESTRING (-3636954.77 7750916.26, -3168756.90 7966747.98, -3124795.45 7893415.62)"),
GeometryRow("POLYGON ((-2299937.47 8474247.90, -2543511.83 8425946.52, -2488034.02 8322274.98, -2299937.47 8474247.90))"))
val df = spark.createDataFrame(data)
.select(ST.geomFromText($"wkt", F.lit(54008)).alias("geometry"))
.withColumn("geodesic_buffer", ST.geodesicBuffer($"geometry", 60000))
.withColumn("buffer_area", F.round(ST.geodesicArea($"geodesic_buffer"),3))
df.select("geodesic_buffer", "buffer_area").show()+--------------------+------------------+
| geodesic_buffer| buffer_area|
+--------------------+------------------+
|{"rings":[[[-2455...|1.1288992603518E10|
|{"rings":[[[-2947...|3.1841572796083E10|
|{"rings":[[[-3641...|6.1757784805281E10|
|{"rings":[[[-2222...|5.9119409521289E10|
+--------------------+------------------+Version table
| Release | Notes |
|---|---|
1.0.0 | Python and SQL functions introduced |
1.5.0 | Scala function introduced |
1.6.0 | distance parameter accepts values with specified units |