Calculate Field calculates field values on a new or existing field. The output will always be a new DataFrame.
Usage notes
-
Calculate Field runs on any DataFrame. A geometry column can be used in calculations but is not required.
-
Calculate Field will always create a new DataFrame. It will not modify the input. You can only calculate values for a single field at a time.
-
You can calculate values for an existing field or for a new field by creating a unique field name.
-
Expressions are created using ArcGIS Arcade. See Arcade expressions for more information.
-
Arcade expressions can be track aware. Track-aware expressions require that the input DataFrame has a single timestamp (instant) and that the a track field is specified using
set. To learn more about building track-aware expressions, see Track aware examples.Track Fields() -
Tracks are represented by the unique combination of one or more track fields. For example, if the
flightandI D Destinationfields are used as track identifiers, the recordsID007,SoldenandID007,Tokyowould be in different tracks since they have different values for theDestinationfield. -
Setting
setsegments tracks at a defined interval. For example, if you use a value of 1 day forTime Boundary Split() time_, and a value of 9:00 a.m. on January 1, 1990 for theboundary_ split time_parameter, each track will be truncated at 9:00 a.m. every day and analyzed within that segment. This split reduces computing time, as it creates smaller tracks for analysis. If splitting by a recurring time interval boundary makes sense for your analysis, it is recommended for big data processing.boundary_ reference
Limitations
-
Only one field can be modified at a time.
-
Calculate Field will always produce a new DataFrame, and will not edit your input DataFrame.
Results
The result is the input DataFrame with a new column appended or an existing column replaced.
Performance notes
Improve the performance of Calculate Field by doing one or more of the following:
-
Only analyze the records in your area of interest. You can pick the records of interest by using one of the following SQL functions:
- ST_Intersection—Clip to an area of interest represented by a polygon. This will modify your input records.
- ST_BboxIntersects—Select records that intersect an envelope.
- ST_EnvIntersects—Select records having an evelope that intersects the envelope of another geometry.
- ST_Intersects—Select records that intersect another dataset or area of intersect represented by a polygon.
- If you are using tracks, split your tracks by using
set.Time Boundary Split()
Similar capabilities
The following tools perform similar capabilities:
You can also perform field calculations directly on your DataFrame with Spark SQL.
Syntax
For more details, go to the GeoAnalytics Engine API reference for calculate field.
| Setter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
run(dataframe) | Runs the Calculate Field tool using the provided DataFrame. | Yes |
set | Sets an Arcade expression used to calculate the new field values. | Yes |
set | Sets the name and type of the new field. | Yes |
set | Sets boundaries to limit calculations to defined spans of time. | No |
set | Sets one or more fields used to identify distinct tracks. | No |
Examples
Run Calculate Field
# Log in
import geoanalytics
geoanalytics.auth(username="myusername", password="mypassword")
# Imports
from geoanalytics.tools import CalculateField
from geoanalytics.sql import functions as ST
from pyspark.sql import functions as F
# Path to the Atlantic hurricanes data
data_path = r"https://sampleserver6.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/rest/services/Hurricanes/MapServer/0"
# Create an Atlantic hurricanes DataFrame
df = spark.read.format("feature-service").load(data_path) \
.st.set_time_fields("Date_Time")
# Use Calculate Field to create a new column containing the average windspeed in
# miles per hour based on the previous, current, and next observation in the track.
result = CalculateField() \
.setField(field_name="avg_windspeed", field_type="DOUBLE") \
.setExpression(expression="Mean($track.field['WINDSPEED'].window(-1,2))") \
.setTrackFields("EVENTID") \
.run(dataframe=df)
# View the first 5 rows of the result DataFrame
result.filter(result["EVENTID"] == "Alberto") \
.select("EVENTID", F.date_format("Date_Time", "yyyy-MM-dd").alias("Date_Time"), "WINDSPEED", "avg_windspeed") \
.sort("avg_windspeed", ascending=False).show(5)
+-------+----------+---------+------------------+
|EVENTID| Date_Time|WINDSPEED| avg_windspeed|
+-------+----------+---------+------------------+
|Alberto|2000-08-12| 110.0|108.33333333333333|
|Alberto|2000-08-12| 110.0|106.66666666666667|
|Alberto|2000-08-13| 105.0|103.33333333333333|
|Alberto|2000-08-12| 100.0| 100.0|
|Alberto|2000-08-13| 95.0| 95.0|
+-------+----------+---------+------------------+
only showing top 5 rowsPlot results
# Get the world continents data for plotting
continents_path = "https://services.arcgis.com/P3ePLMYs2RVChkJx/ArcGIS/rest" \
"/services/World_Continents/FeatureServer/0"
continents_subset_df = spark.read.format("feature-service").load(continents_path) \
.where("""CONTINENT = 'North America' or
CONTINENT = 'South America' or
CONTINENT = 'Europe' or
CONTINENT = 'Africa'""")
# Plot the Alantic hurricanes data with the continents subset data
continents_subset_plot = continents_subset_df.st.plot(facecolor="none",
edgecolors="lightblue",
figsize=(14,8))
result_plot = result.st.plot(cmap_values="avg_windspeed",
cmap="YlOrRd",
legend=True,
ax=continents_subset_plot,
basemap="light")
result_plot.set_title("Alantic hurricanes average windspeed (miles per hour)")
result_plot.set_xlabel("X (Meters)")
result_plot.set_xlim(right=10000000)
result_plot.set_ylabel("Y (Meters)");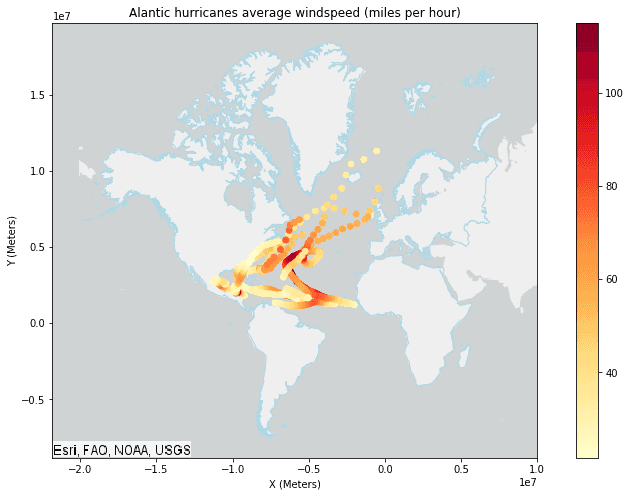
Version table
| Release | Notes |
|---|---|
1.0.0 | Tool introduced |