Learn how to create and display a map with a basemap layer.
A map contains layers of geographic data. A map contains a basemap layer and, optionally, one or more data layers. You can display a specific area of a map by using a map view and setting the location and zoom level.
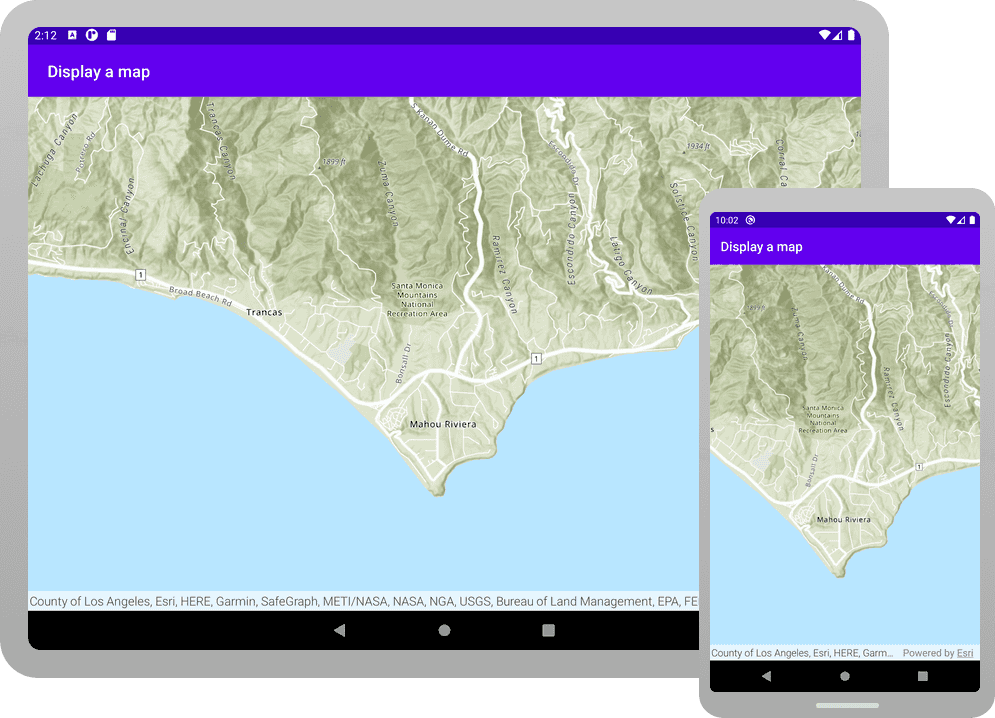
In this tutorial, you create and display a map of the Santa Monica Mountains in California using the topographic basemap layer.
The map and code will be used as the starting point for other 2D tutorials.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial:
-
You need an ArcGIS Location Platform or ArcGIS Online account.
-
A development and deployment environment that meets the system requirements.
-
An IDE for Android development in Kotlin.
Steps
Create a new Android Studio project
Use Android Studio to create an app and configure it to reference the API.
-
Open Android Studio.
-
In the Welcome to Android Studio window, click New Project.
Or if you already have Android Studio opened, click File > New > New Project in the menu bar.
-
In the New Project window, make sure Phone and Tablet tab is selected, and then select Empty Activity. Click Next.
-
In the next window, set the following options and then click Finish.
- Name:
Display a map. - Package name: Change to
com.example.app. Or change to match your organization. - Save location: Set to a new folder.
- Minimum SDK: API 26 ("Oreo"; Android 8.0)
- Build configuration language: Kotlin DSL (build.gradle.kts)
- Name:
-
-
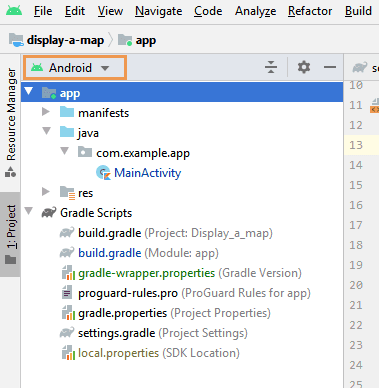
In the Project tool window, make sure that your current view is Android. These tutorial instructions refer to that view.
If your view name is something other than Android (such as Project or Packages), click on the leftmost control in the title bar of the Project tool window, and select Android from the list.
-
From the Project tool window, open Gradle Scripts > build.gradle.kts (Project: Display_a_map). Replace the contents of the file with the following code.
build.gradle.kts (Project: Display_a_map)Use dark colors for code blocks // Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules. plugins { alias(libs.plugins.android.application) apply false alias(libs.plugins.jetbrains.kotlin.android) apply false } -
From the Project tool window, open Gradle Scripts > build.gradle.kts (Module :app). Replace the contents of the file with the entire expanded code below.
build.gradle.kts (Module: app)Use dark colors for code blocks // ArcGIS Maps for Kotlin - SDK dependency implementation(libs.arcgis.maps.kotlin) // Toolkit dependencies implementation(platform(libs.arcgis.maps.kotlin.toolkit.bom)) implementation(libs.arcgis.maps.kotlin.toolkit.geoview.compose) // Additional modules from Toolkit, if needed, such as: // implementation(libs.arcgis.maps.kotlin.toolkit.authentication)The module-level
build.gradle.ktsfile generated by the Android Studio New Project wizard declares Android and Kotlin tool versions that should all work together. The options for the Kotlin Compiler (thekotlinblock) and the Compose Compiler (theOptions composeblock) must be compatible. You can confirm compatibility by consulting Android's Compose to Kotlin Compatibility Map.Options build.gradle.kts (Module: app)Use dark colors for code blocks Copy kotlinOptions { jvmTarget = "17" } composeOptions { kotlinCompilerExtensionVersion = "1.5.11" } -
From the Project tool window, open Gradle Scripts > libs.versions.toml. In the
[versions]section, you need to declare the version number for ArcGIS Maps SDK for Kotlin. And in the[libraries]section, you need to add the library declarations for the following:- the ArcGIS Maps SDK for Kotlin SDK.
- the ArcGIS Maps SDK for Kotlin Toolkit BOM.
- any Toolkit components needed. For this tutorial, you need only the
geoview-composecomponent, which contains the composableMapView.
The version for the Toolkit BOM applies to all the Toolkit components you declare.
Gradle version catalogs are the standard Android approach to declaring dependency versions. They are preferred over specifying versions numbers in the
build.gradle.ktsor listing version numbers in aversion.gradle. In recent releases of Android Studio, the New Project Wizard generatesbuild.gradle.ktsandgradle/libs.versions.tomlfiles that support this standard.Gradle version catalogs can also use BOM files to specify a single version number for all artifacts in the BOM. For more details, see
Using the BOMin theREADMEof the ArcGIS Maps SDK for Kotlin Toolkit.gradle/libs.versions.tomlUse dark colors for code blocks Copy [versions] arcgisMapsKotlin = "200.5.0" [libraries] arcgis-maps-kotlin = { group = "com.esri", name = "arcgis-maps-kotlin", version.ref = "arcgisMapsKotlin" } arcgis-maps-kotlin-toolkit-bom = { group = "com.esri", name = "arcgis-maps-kotlin-toolkit-bom", version.ref = "arcgisMapsKotlin" } arcgis-maps-kotlin-toolkit-geoview-compose = { group = "com.esri", name = "arcgis-maps-kotlin-toolkit-geoview-compose" } # Additional modules from Toolkit, if needed, such as: # arcgis-maps-kotlin-toolkit-authentication = { group = "com.esri", name = "arcgis-maps-kotlin-toolkit-authentication" } -
From the Project tool window, open Gradle Scripts > settings.gradle.kts. Replace the contents of the file with the expanded code below.
settings.gradle.kts (Display a map)Use dark colors for code blocks dependencyResolutionManagement { repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS) repositories { google() mavenCentral() maven { url = uri("https://esri.jfrog.io/artifactory/arcgis") } } } rootProject.name = "Display a map" include(":app") -
Sync the Gradle changes. Click the Sync now prompt or click the refresh icon (Sync Project with Gradle Files) in the toolbar. This may take several minutes.
-
From the Project tool window, open app > manifests > AndroidManifest.xml. Update the Android manifest to allow internet access.
Insert these new elements within the
manifestelement. Do not alter or remove any other statements.Depending on what ArcGIS functionality you add in future tutorials, it is likely you will need to add additional permissions to your manifest.
AndroidManifest.xmlUse dark colors for code blocks 3 4 5Add line. <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
Create a map
-
From the Project tool window, right click on app > kotlin+java > com.example.app, select New > package from the list. Enter com.example.app.screens as the package name. Hit Enter on your keyboard. This step creates a new package that will contain all the UI files.
-
Right click on the screens package you just created, select New > Kotlin Class/File from the list. In the pop-up window, select File and enter MainScreen as the file name. Hit Enter on your keyboard.
-
In MainScreen.kt, delete any lines of code that were inserted automatically by Android Studio. Then add the following OptIn annotation, package name, and imports.
MainScreen.ktUse dark colors for code blocks @file:OptIn(ExperimentalMaterial3Api::class) package com.example.app.screens import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding import androidx.compose.material3.ExperimentalMaterial3Api import androidx.compose.material3.Scaffold import androidx.compose.material3.Text import androidx.compose.material3.TopAppBar import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.runtime.remember import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.res.stringResource import com.arcgismaps.mapping.ArcGISMap import com.arcgismaps.mapping.BasemapStyle import com.arcgismaps.mapping.Viewpoint import com.arcgismaps.toolkit.geoviewcompose.MapView import com.example.app.R -
Create a top-level function named
createthat returns anMap() ArcGISMap.MainScreen.ktUse dark colors for code blocks fun createMap(): ArcGISMap { } -
Create an
ArcGISMapusing theBasemapStyle.ArcGISTopographic, and callapply {}on the map. The function returns thisArcGISMap.For more information on
apply {}, see Kotlin scope functions.MainScreen.ktUse dark colors for code blocks fun createMap(): ArcGISMap { return ArcGISMap(BasemapStyle.ArcGISTopographic).apply { } } -
In the
applyblock, create aViewpointwith x (longitude) and y (latitude) coordinates, and a scale. Assign the view point to theinitialproperty of theViewpoint ArcGISMap.MainScreen.ktUse dark colors for code blocks fun createMap(): ArcGISMap { return ArcGISMap(BasemapStyle.ArcGISTopographic).apply { initialViewpoint = Viewpoint( latitude = 34.0270, longitude = -118.8050, scale = 72000.0 ) } }
Create a MainScreen to hold the map
-
Create a composable function named
Main, which will callScreen MapView.MainScreen.ktUse dark colors for code blocks @Composable fun MainScreen() { } -
Add a
rememberblock and callcreateinside it. Then assignMap() rememberto a local variable namedmap.The top-level composable function
rememberis used to retain state across recompositions.MainScreen.ktUse dark colors for code blocks @Composable fun MainScreen() { val map = remember { createMap() } } -
You will now call several composable functions from Android Jetpack Compose. Call
Scaffoldand pass aTopwith aApp Bar Textthat contains the app name (R.string.app)._name MainScreen.ktUse dark colors for code blocks @Composable fun MainScreen() { val map = remember { createMap() } Scaffold( topBar = { TopAppBar(title = { Text(text = stringResource(id = R.string.app_name)) }) } ) { } } -
In the trailing lambda for
Scaffold, call theMapViewcomposable defined in the ArcGIS Maps SDK for Kotlin Toolkit. Pass a Modifier that has maximum size and default padding. And passmapas thearcparameter.GIS Map MainScreen.ktUse dark colors for code blocks @Composable fun MainScreen() { val map = remember { createMap() } Scaffold( topBar = { TopAppBar(title = { Text(text = stringResource(id = R.string.app_name)) }) } ) { MapView( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize().padding(it), arcGISMap = map ) } }
Call MainScreen inside MainActivity class
-
Open the app > kotlin+java > com.example.app > MainActivity.kt. Delete all lines of code except for the package declaration (the first line) and the
Mainclass definition.Activity MainActivity.ktUse dark colors for code blocks Copy package com.example.app class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() { } -
Add import statements to MainActivity.kt.
MainActivity.ktUse dark colors for code blocks package com.example.app import android.os.Bundle import androidx.activity.ComponentActivity import androidx.activity.compose.setContent import com.arcgismaps.ApiKey import com.arcgismaps.ArcGISEnvironment import com.example.app.screens.MainScreen import com.example.app.ui.theme.DisplayAMapTheme class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() { } -
In the
setblock of theContent() onlifecycle function, you will call the composable functionCreate() Main, with default theming applied. To do this, addScreen onwith the following code.Create() MainActivity.ktUse dark colors for code blocks class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContent { DisplayAMapTheme { MainScreen() } } } }
Get an access token
You need an access token to use the location services used in this tutorial.
-
Go to the Create an API key tutorial to obtain an access token.
-
Ensure that the following privilege is enabled: Location services > Basemaps > Basemap styles service.
-
Copy the access token as it will be used in the next step.
To learn more about other ways to get an access token, go to Types of authentication.
Set an API Key
-
In the
Mainclass, create theActivity setmethod, where you set theApi Key() ArcGISEnvironment.apiKeyproperty by callingApiKey.create()and passing your access token as a string. Don't forget the double quotes.MainActivity.ktUse dark colors for code blocks class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContent { DisplayAMapTheme { MainScreen() } } } private fun setApiKey() { ArcGISEnvironment.apiKey = ApiKey.create("YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN") } } -
Call
setin theApi Key() onlifecycle method, beforeCreate() set.Content {} MainActivity.ktUse dark colors for code blocks class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setApiKey() setContent { DisplayAMapTheme { MainScreen() } } } private fun setApiKey() { ArcGISEnvironment.apiKey = ApiKey.create("YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN") } }
Run your app
-
Click Run > Run > app to run the app.
In Android Studio, you have two choices for running your app: an actual Android device or the Android Emulator.
Android device
Connect your computer to your Android device, using USB or Wi-Fi. For more details, see How to connect your Android device.
Android Emulator
Create an AVD (Android Virtual Device) to run in the Android Emulator. For details, see Run apps on the Android Emulator.
Selecting a device
When you build and run an app in Android Studio, you must first select a device. From the Android Studio toolbar, you can access the drop-down list of your currently available devices, both virtual and physical.
 .
.If you cannot access the list on the toolbar, click Tools > Device Manager.
You should see a map with the topographic basemap layer centered on the Santa Monica Mountains in California. Pinch, drag, and double-tap the map view to explore the map.
What's next?
Learn how to use additional API features, ArcGIS location services, and ArcGIS tools in these tutorials: