Calculate a geodesic path between two points and measure its distance.
Use case
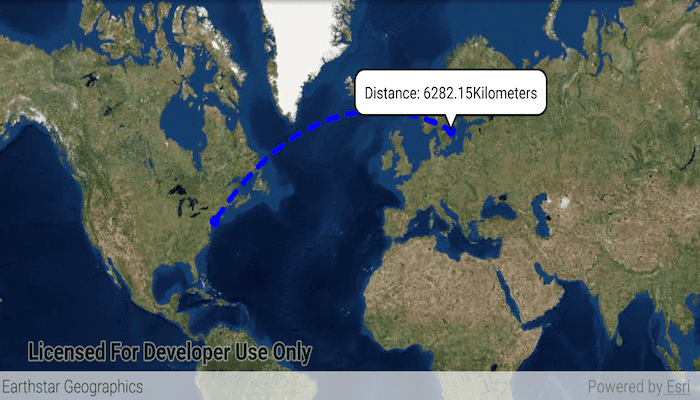
A geodesic distance provides an accurate, real-world distance between two points. Visualizing flight paths between cities is a common example of a geodesic operation since the flight path between two airports takes into account the curvature of the earth, rather than following the planar path between those points, which appears as a straight line on a projected map.
How to use the sample
Tap anywhere on the map. A line graphic will display the geodesic line between the two points. In addition, text that indicates the geodesic distance between the two points will be updated. Tap elsewhere and a new line will be created.
How it works
- Create a
Pointand display it as aGraphic. - Obtain a new point when a tap occurs on the
MapViewand add this point as a graphic. - Create a
Polylinefrom the two points. - Execute
GeometryEngine.densifyGeodetic(...)by passing in the created polyine then create a graphic from the returnedGeometry. - Execute
GeometryEngine.lengthGeodetic(...)by passing in the two points and display the returned length on the screen.
Relevant API
- GeometryEngine.densifyGeodetic
- GeometryEngine.lengthGeodetic
About the data
The Imagery basemap provides the global context for the displayed geodesic line.
Tags
densify, distance, geodesic, geodetic
Sample Code
/* Copyright 2018 Esri
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
*/
package com.esri.arcgisruntime.sample.geodesicoperations
import android.graphics.Color
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.MotionEvent
import android.widget.TextView
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.ArcGISRuntimeEnvironment
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.GeodeticCurveType
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.GeometryEngine
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.LinearUnit
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.LinearUnitId
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.Point
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.PointCollection
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.Polyline
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.geometry.SpatialReferences
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.ArcGISMap
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.BasemapStyle
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.DefaultMapViewOnTouchListener
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.Graphic
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.GraphicsOverlay
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.mapping.view.MapView
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.symbology.SimpleLineSymbol
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.symbology.SimpleMarkerSymbol
import com.esri.arcgisruntime.sample.geodesicoperations.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
import kotlin.math.roundToInt
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val srWgs84 = SpatialReferences.getWgs84()
private val unitOfMeasurement = LinearUnit(LinearUnitId.KILOMETERS)
private val units = "Kilometers"
private val activityMainBinding by lazy {
ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
}
private val mapView: MapView by lazy {
activityMainBinding.mapView
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(activityMainBinding.root)
// authentication with an API key or named user is required to access basemaps and other
// location services
ArcGISRuntimeEnvironment.setApiKey(BuildConfig.API_KEY)
// create a map
val map = ArcGISMap(BasemapStyle.ARCGIS_IMAGERY)
// set a map to a map view
mapView.map = map
// create a graphic overlay
val graphicOverlay = GraphicsOverlay()
mapView.graphicsOverlays.add(graphicOverlay)
// add a graphic at JFK to represent the flight start location
val start = Point(-73.7781, 40.6413, srWgs84)
val locationMarker =
SimpleMarkerSymbol(SimpleMarkerSymbol.Style.CIRCLE, 0xFF0000FF.toInt(), 10f)
val startLocation = Graphic(start, locationMarker)
// create a graphic for the destination
val endLocation = Graphic()
endLocation.symbol = locationMarker
// create a graphic representing the geodesic path between the two locations
val path = Graphic()
path.symbol = SimpleLineSymbol(SimpleLineSymbol.Style.DASH, 0xFF0000FF.toInt(), 5f)
// add graphics to graphics overlay
graphicOverlay.graphics.apply {
add(startLocation)
add(endLocation)
add(path)
}
// create listener to get the location of the tap in the screen
mapView.onTouchListener = object : DefaultMapViewOnTouchListener(this, mapView) {
override fun onSingleTapConfirmed(e: MotionEvent): Boolean {
// get the point that was clicked and convert it to a point in the map
val clickLocation = android.graphics.Point(e.x.roundToInt(), e.y.roundToInt())
val mapPoint = mapView.screenToLocation(clickLocation)
val destination = GeometryEngine.project(mapPoint, SpatialReferences.getWgs84())
endLocation.geometry = destination
// create a straight line path between the start and end locations
val points = PointCollection(listOf(start, destination as Point), srWgs84)
val polyLine = Polyline(points)
// densify the path as a geodesic curve with the path graphic
val pathGeometry = GeometryEngine.densifyGeodetic(
polyLine,
1.0,
unitOfMeasurement,
GeodeticCurveType.GEODESIC
)
path.geometry = pathGeometry
// calculate path distance
val distance =
GeometryEngine.lengthGeodetic(
pathGeometry,
unitOfMeasurement,
GeodeticCurveType.GEODESIC
)
// create a textView for the callout
val calloutContent = TextView(applicationContext)
calloutContent.setTextColor(Color.BLACK)
calloutContent.setSingleLine()
// format coordinates to 2 decimal places
val distanceString = String.format("%.2f", distance)
// display distance as a callout
calloutContent.text = "Distance: $distanceString $units"
val callout = mapView.callout
callout.location = mapPoint
callout.content = calloutContent
callout.show()
return true
}
}
}
override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
mapView.pause()
}
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
mapView.resume()
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
mapView.dispose()
}
}