Display annotation from a feature service URL.
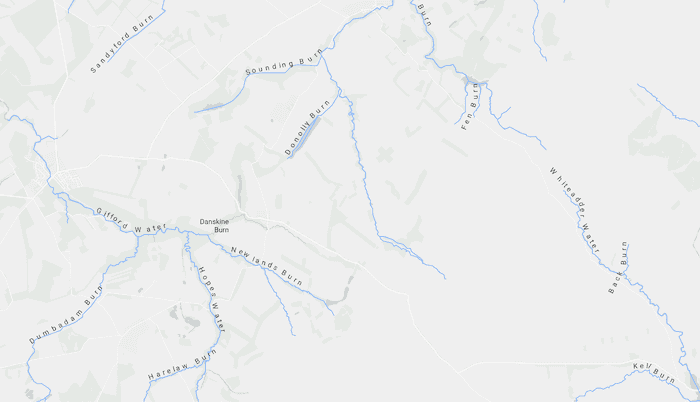
Use case
Annotation is useful for displaying text that you don't want to move or resize when the map is panned or zoomed (unlike labels which will move and resize). You can use annotation to place text at a fixed size, position, orientation, font, and so on. You may choose to do this for cartographic reasons or because the exact placement of the text is important.
How to use the sample
Pan and zoom to see names of waters and burns in a small region of Scotland.
How it works
- Create an
ArcGISMapwith a light gray canvas basemap and a viewpoint near the data. - Create a
FeatureLayerfrom a feature service URL. - Create an
AnnotationLayerfrom a feature service URL. - Add both layers to the operational layers of the map and display it in a
MapView.
Relevant API
- AnnotationLayer
- FeatureLayer
About the data
Data derived from the OS Open Rivers dataset from Ordnance Survey. Contains OS data © Crown copyright and database right 2018.
The annotation layer contains two sublayers of rivers in East Lothian, Scotland, which were set by the author to only be visible within the following scale ranges:
- Water (1:50,000 - 1:100,000) - A large stream, as defined in the Scots language
- Burn (1:25,000 - 1:75,000) - A brook or small stream, as defined in the Scots language
Additional information
Annotation is only supported from feature services hosted on ArcGIS Enterprise.
Tags
annotation, cartography, labels, placement, reference scale, text, utility
Sample Code
/* Copyright 2025 Esri
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
*/
package com.esri.arcgismaps.sample.displayannotation.components
import android.app.Application
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.lifecycle.AndroidViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope
import com.arcgismaps.data.ServiceFeatureTable
import com.arcgismaps.mapping.ArcGISMap
import com.arcgismaps.mapping.BasemapStyle
import com.arcgismaps.mapping.Viewpoint
import com.arcgismaps.mapping.layers.AnnotationLayer
import com.arcgismaps.mapping.layers.FeatureLayer
import com.esri.arcgismaps.sample.sampleslib.components.MessageDialogViewModel
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class DisplayAnnotationViewModel(app: Application) : AndroidViewModel(app) {
// URL to the feature service for rivers in East Lothian
private val eastLothianRiversUrl =
"https://services1.arcgis.com/6677msI40mnLuuLr/arcgis/rest/services/East_Lothian_Rivers/FeatureServer/0"
// URL to the annotation feature service for rivers in East Lothian
private val riversAnnotationUrl =
"https://sampleserver6.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/rest/services/RiversAnnotation/FeatureServer/0"
// ServiceFeatureTable for the rivers feature service
private val featureTable: ServiceFeatureTable = ServiceFeatureTable(eastLothianRiversUrl)
// FeatureLayer created from the ServiceFeatureTable
private val featureLayer: FeatureLayer = FeatureLayer.createWithFeatureTable(featureTable)
// AnnotationLayer created from the annotation service URL
private val annotationLayer: AnnotationLayer = AnnotationLayer(riversAnnotationUrl)
// ArcGISMap with a light gray canvas basemap and initial viewpoint (East Lothian, Scotland)
val arcGISMap by mutableStateOf(
ArcGISMap(BasemapStyle.ArcGISLightGray).apply {
initialViewpoint = Viewpoint(
latitude = 55.882436,
longitude = -2.725610,
scale = 72223.819286
)
// Add both layers to the operational layers before loading
operationalLayers.addAll(listOf(featureLayer, annotationLayer))
}
)
// Message dialog for error handling
val messageDialogVM = MessageDialogViewModel()
init {
viewModelScope.launch {
// Listen for load failures on the feature layer
featureLayer.load().onFailure {
messageDialogVM.showMessageDialog(it)
}
// Listen for load failures on the annotation layer
annotationLayer.load().onFailure {
messageDialogVM.showMessageDialog(it)
}
}
}
}