With the ArcGIS Maps SDK for Kotlin, you can perform advanced operations on the composable MapView and SceneView components using proxy classes like MapViewProxy and SceneViewProxy. The proxy classes provides access to methods and properties that aren't suitable for use in a composable function's initializer or a modifier. They enable operations such as:
- Identifying features on the map.
- Setting the viewpoint with animation.
- Converting coordinates between the map and screen.
- Exporting a snapshot of the view's image.
To use a proxy, you must first create a one-to-one relationship between it and the composable view. This is done by passing a proxy instance to the composable Map or Scene function.
MapView(
arcGISMap = map,
graphicsOverlays = listOf(mapViewModel.graphicsOverlay),
mapViewProxy = mapViewModel.mapViewProxy
)
Note: The example above shows a Map that uses a Map. Similarly, you would use a Scene with a Scene.
Identify features
The following example demonstrates how to use the Map to identify features on a map. When a user taps the screen, the identify method is called to retrieve features at that location and display their associated popups or attributes.
// In the ViewModel:
class MapViewModel(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
// ....
// Proxy object used to help identify the feature at the tapped coordinate
val mapViewProxy = MapViewProxy()
fun identifyFeatureAt(
screenCoordinate: ScreenCoordinate,
onFeatureSelected: (ArcGISFeature) -> Unit
) {
viewModelScope.launch {
// Identify the feature tapped at the given screen coords
val identifyLayerResults = mapViewProxy.identifyLayers(
screenCoordinate = screenCoordinate,
tolerance = 5.dp,
returnPopupsOnly = false,
maximumResults = 1
).getOrThrow()
// Identify the layer
val identifyLayerResult = identifyLayerResults.firstOrNull()
// Identify the feature
val foundFeature = identifyLayerResult?.geoElements?.firstOrNull() as? ArcGISFeature
if (foundFeature != null) {
// Report the selected feature to UI
onFeatureSelected(foundFeature)
}
}
}
// In the Composable:
@Composable
fun MainScreen(modifier: Modifier, viewmodel: MapViewModel = viewModel()) {
var selectedFeature by remember { mutableStateOf<ArcGISFeature?>(null) }
MapView(
modifier = modifier.fillMaxSize(),
arcGISMap = viewmodel.map,
mapViewProxy = viewmodel.mapViewProxy,
onSingleTapConfirmed = { tapEvent ->
viewmodel.identifyFeatureAt(
screenCoordinate = tapEvent.screenCoordinate,
onFeatureSelected = { feature ->
selectedFeature = feature
}
)
}
) {
}
}
Set a Viewpoint
You can use the Map to programmatically change the viewpoint of the map. This is useful for things like zooming to a specific feature or panning to a new location.
// Identify the feature
val foundFeature = identifyLayerResult?.geoElements?.firstOrNull() as? ArcGISFeature
if (foundFeature != null) {
// Animate the viewpoint to center on the feature.
foundFeature.geometry?.let { centerPoint ->
mapViewProxy.setViewpointAnimated(
viewpoint = Viewpoint(centerPoint),
duration = 300.milliseconds,
curve = AnimationCurve.EaseOutSine
)
}
// Report the selected feature to UI
onFeatureSelected(foundFeature)
}
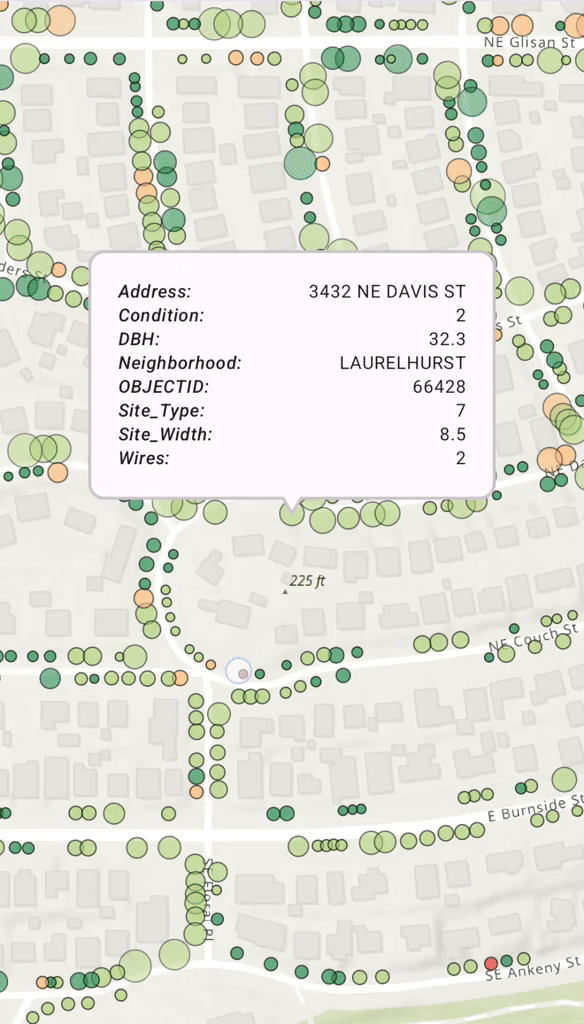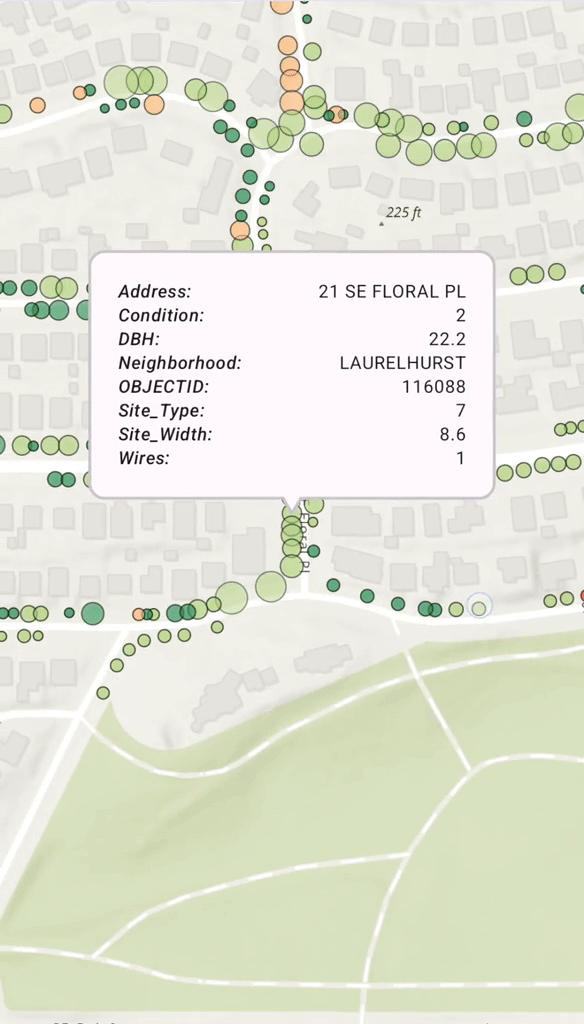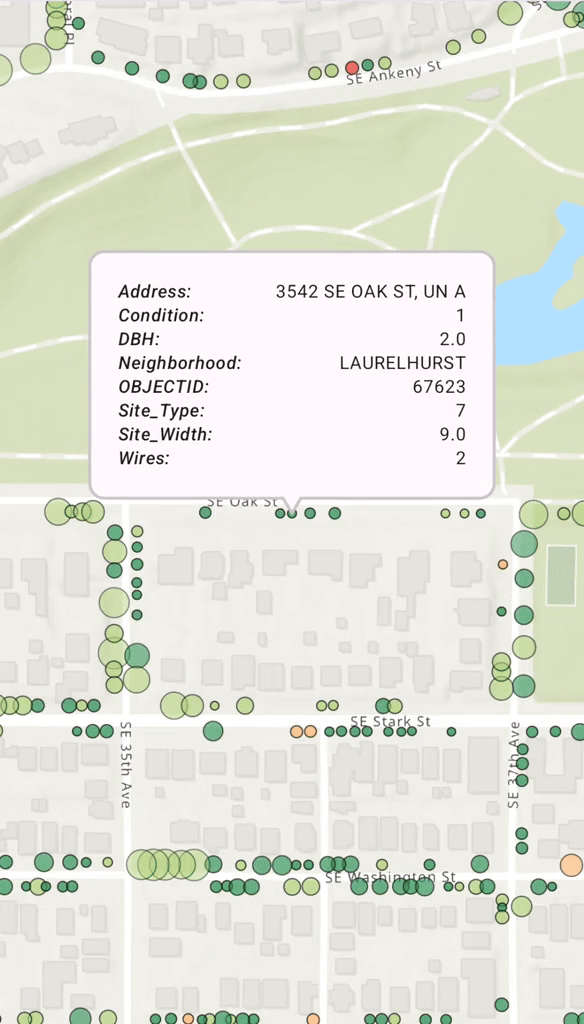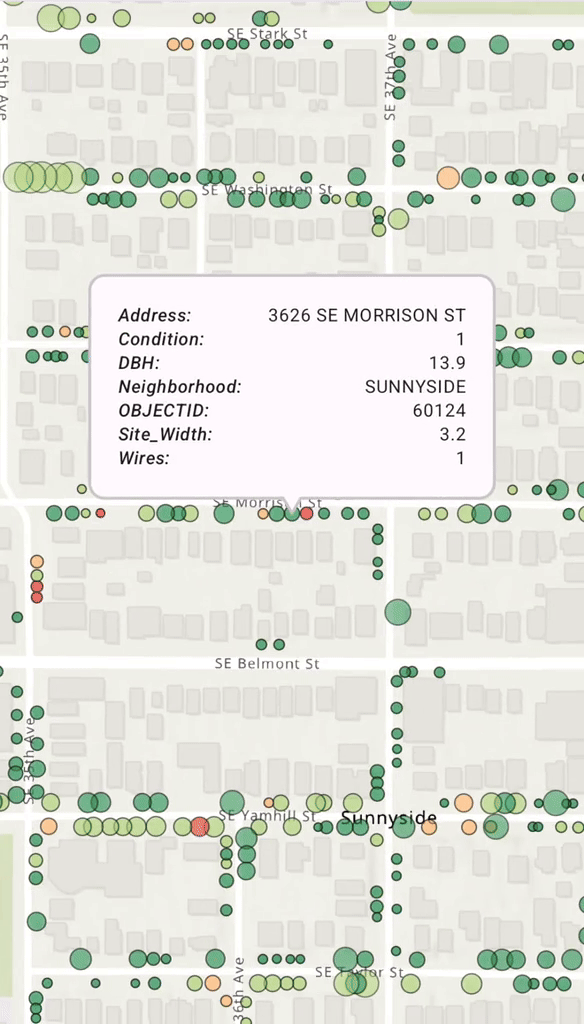
Display a Callout on a GeoElement
When a user taps on a map and a feature is identified, you often want to display a Popup, or Callout, to show more information. You can use a mutable property in your ViewModel to hold the identified Geo. When this property is updated, Compose automatically recomposes the UI and displays the Callout.
The following example combines the above patterns to create a full workflow.
- A user taps the map, triggering the
onevent handler.Single Tap Confirmed - The ViewModel's
identifyfunction is called, which uses theFeature At Mapto find a feature at the tapped location.View Proxy - The
setfunction is used to gracefully move the map's viewpoint to the identified feature.Viewpoint Animated - The ViewModel updates its
selectedstate.Feature - Compose detects the state change and displays a
Calloutat the feature's location, using its attributes to populate the content.
This seamless pattern demonstrates how Map and composable state work together to build a responsive and interactive user experience.
// In the Composable:
@Composable
fun MainScreen(modifier: Modifier, viewmodel: MapViewModel = viewModel()) {
var selectedFeature by remember { mutableStateOf<ArcGISFeature?>(null) }
MapView(
modifier = modifier.fillMaxSize(),
arcGISMap = viewmodel.map,
mapViewProxy = viewmodel.mapViewProxy,
onSingleTapConfirmed = { tapEvent ->
viewmodel.identifyFeatureAt(
screenCoordinate = tapEvent.screenCoordinate,
onFeatureSelected = { feature ->
selectedFeature = feature
}
)
}
) {
selectedFeature?.let { selectedFeature ->
Callout(geoElement = selectedFeature) {
CalloutContent(
selectedElementAttributes = viewmodel.filterAttributes(
attributes = selectedFeature.attributes
)
)
}
}
}
}
@Composable
fun CalloutContent(selectedElementAttributes: Map<String, Any?>) {
LazyColumn(
modifier = Modifier.widthIn(max = 250.dp),
contentPadding = PaddingValues(8.dp)
) {
selectedElementAttributes.forEach { attribute ->
item {
Row(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceBetween,
verticalAlignment = Alignment.Top
) {
Text(
text = "${attribute.key}:",
fontStyle = FontStyle.Italic,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.labelMedium
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.width(20.dp))
Text(
text = "${attribute.value}",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodySmall,
textAlign = TextAlign.End
)
}
}
}
}
}
Note:
- See the tutorial guide Display device location to learn how to display the current device location on a map or scene.
- See the sample app Identify layer features to learn how to identify features in all layers in a map.
- See the sample app Show popup to learn how to show a predefined popup from a web map.
- See the sample app Show callout to learn how to show a callout with the latitude and longitude of user-tapped points.