Learn how to create and display a map with a basemap layer.
A map contains layers of geographic data. A map contains a basemap layer and, optionally, one or more data layers. You can display a specific area of a map by using a map view and setting the location and zoom level.
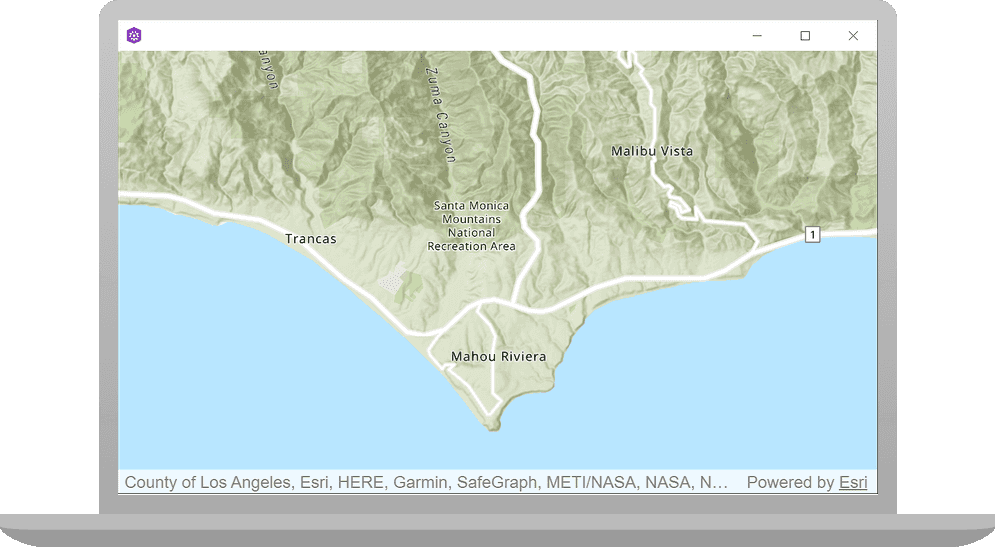
In this tutorial, you create and display a map of the Santa Monica Mountains in California using the topographic basemap layer.
The map and code will be used as the starting point for other 2D tutorials.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial:
-
You need an ArcGIS Location Platform or ArcGIS Online account.
-
Your system meets the system requirements.
-
The ArcGIS Maps SDK for Qt, version 200.4.0 or later is installed.
-
The Qt 6.5.1 software development framework is installed.
Create a new ArcGIS Maps Qt Creator Project
Use Qt Creator to create an app that displays a Map centered on the Santa Monica Mountains.
-
Start Qt Creator.
-
Click File > New File or Project. Under Projects, select ArcGIS.
-
Select the ArcGIS Maps 200.4.0 Qt Quick C++ app project template (or a later version) and click Choose.
You may have several selections for the ArcGIS project type. Be sure to select ArcGIS Maps 200.4.0 Qt Quick C++ app (or a later version).
-
In the Project Location dialog, name your project display_a_map. Click Next.
-
In the Define Build System dialog, select qmake for your build system. Click Next.
-
In the Define Project Details dialog, give this app a description or leave as is. Leave the rest of this dialog as is.
-
Leave the 3D project box unchecked. At the ArcGIS Online Basemap dropdown menu, select Topographic. Then click Next.
-
On the Kit Selection dialog, check the kit(s) you previously set up when you installed the API. You should select a Desktop kit to run this tutorial. Then click Next.
-
At the Project Management dialog, the option to Add as a subproject to root project is only available if you have already created a root project. Ignore this dialog for this tutorial. Click Next.
Get an access token
You need an access token to use the location services used in this tutorial.
-
Go to the Create an API key tutorial to obtain an access token.
-
Ensure that the following privilege is enabled: Location services > Basemaps > Basemap styles service.
-
Copy the access token as it will be used in the next step.
To learn more about other ways to get an access token, go to Types of authentication.
Set your API key
In the Projects window, in the Sources folder, open the main.cpp file. Modify the code to set the API key. Paste the access token between the double quotes. Save and close the file.
// 2. API key authentication: Get a long-lived access token that gives your application access to
// ArcGIS location services. Go to the tutorial at https://links.esri.com/create-an-api-key.
// Copy the API Key access token.
const QString accessToken = QString("");
Add a map
Use the map view to display a map centered on the Santa Monica Mountains in California. The map will contain a layer built from the ArcGISTopographic BasemapStyle.
-
In the Projects window, open the Headers folder. Double-click the file display_a_map.h to open it.
-
Add the declaration
void setupunderViewpoint(); private:. Then save and close the file.Display_a_map.hUse dark colors for code blocks Add line. private: Esri::ArcGISRuntime::MapQuickView* mapView() const; void setMapView(Esri::ArcGISRuntime::MapQuickView* mapView); void setupViewpoint(); -
In the Projects window, open the Sources folder. Open the display_a_map.cpp file.
-
Add the following
#includestatements.Display_a_map.cppUse dark colors for code blocks Add line. Add line. Add line. Add line. #include "Display_a_map.h" #include "Map.h" #include "MapTypes.h" #include "MapQuickView.h" #include "Point.h" #include "Viewpoint.h" #include "SpatialReference.h" #include <QFuture>
Create the view point
-
Add code to implement the
setupmethod. This method creates aViewpoint centerPointbased on aSpatialReferencealong with longitude and latitude. It also creates aViewpointbased oncenterand sets scale. Lastly, it asynchronously sets the initialMapviewpoint.The center
Pointand scale value keep the initialViewpointcentered and focused on the Santa Monica Mountains. The scale value sets the level of detail to focus on the area of interest.The spatial reference created above is set to use World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84), the spatial reference commonly used for GPS, and it has the well known id
4326. To learn more, seeSpatial Referencesin the ArcGIS Maps SDK for Qt Guide.Display_a_map.cppUse dark colors for code blocks Add line. Add line. Add line. Add line. Add line. Add line. Add line. Add line. MapQuickView* Display_a_map::mapView() const { return m_mapView; } void Display_a_map::setupViewpoint() { const Point center(-118.80543, 34.02700, SpatialReference::wgs84()); const Viewpoint viewpoint(center, 100000.0); m_mapView->setViewpointAsync(viewpoint); }The
setmethod appearing later in this file gets a handle to theM a p View Mapobject that was declared in QML code and sets theView Mapon theMapfor display. This code is installed by the templates that ArcGIS provides when creating a new project in Qt. You should not modify it.View -
Add the following line of code to call
setup.Viewpoint Display_a_map.cppUse dark colors for code blocks Add line. // Set the view (created in QML) void Display_a_map::setMapView(MapQuickView* mapView) { if (!mapView || mapView == m_mapView) { return; } m_mapView = mapView; m_mapView->setMap(m_map); setupViewpoint(); -
Press Ctrl + R to run the app.
You should see a map with the topographic basemap layer centered on the Santa Monica Mountains in California. Zoom in and out, and drag the map view to explore the map.
What's next?
Learn how to use additional API features, ArcGIS location services, and ArcGIS tools in these tutorials: