Learn how to implement user authentication to access a secure ArcGIS service with OAuth credentials.
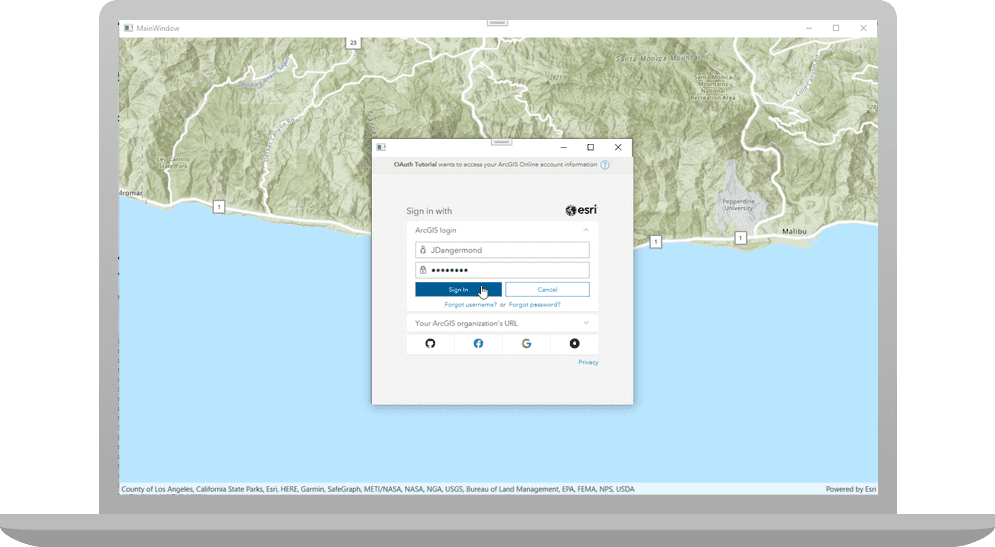
You can use different types of authentication to access secured ArcGIS services. To implement OAuth credentials for user authentication, you can use your ArcGIS account to register an app with your portal and get a Client ID, and then configure your app to redirect users to login with their credentials when the service or content is accessed. This is known as user authentication. If the app uses premium ArcGIS Online services that consume credits, for example, the app user's account will be charged.
In this tutorial, you will build an app that implements user authentication using OAuth credentials so users can sign in and be authenticated through ArcGIS Online to access the ArcGIS World Traffic service.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial:
-
You need an ArcGIS Location Platform or ArcGIS Online account.
-
Ensure your development environment meets the system requirements.
Optionally, you may want to install the ArcGIS Maps SDK for .NET to get access to project templates in Visual Studio (Windows only) and offline copies of the NuGet packages.
Set up authentication
To access the secure ArcGIS location services used in this tutorial, you will implement user authentication. When your app runs, the user will be prompted to authenticate with an ArcGIS Location Platform or an ArcGIS Online account.
You can implement API key authentication or user authentication in your Maps SDK for .NET apps. Compare the differences below:
API key authentication
- Users are not required to sign in.
- Requires creating an API key credential with the correct privileges.
- API keys are long-lived access tokens.
- Service usage is billed to the API key owner/developer.
- Simplest authentication method to implement.
- Recommended approach for new ArcGIS developers.
Learn more in API key authentication.
User authentication
- Users are required to sign in with an ArcGIS account.
- User accounts must have privilege to access the ArcGIS services used in application.
- Requires creating OAuth credentials.
- Application uses a redirect URL and client ID.
- Service usage is billed to the organization of the user signed into the application.
Learn more in User authentication.
Create a new OAuth credential to access the secure resources used in this tutorial.
-
Complete the Create OAuth credentials for user authentication tutorial.
-
Copy and paste the ClientID and RedirectURL into a safe location. They will be used in a later step.
All users that access this application need account privileges to access the basemap styles service.
The Client ID uniquely identifies your app on the authenticating server. If the server cannot find an app with the provided Client ID, it will not proceed with authentication.
The Redirect URL (also referred to as a callback url) is used to identify a response from the authenticating server when the system returns control back to your app after an OAuth login. Since it does not necessarily represent a valid endpoint that a user could navigate to, the redirect URL can use a custom scheme, such as my-app. You can configure several redirect URLs in your application definition and can remove or edit them. It's important to make sure the redirect URL used in your app's code matches a redirect URL configured for the application.
Develop or download
You have two options for completing this tutorial:
Option 1: Develop the code
Create a new Visual Studio Project
ArcGIS Maps SDK for .NET supports apps for Windows Presentation Framework (WPF), Universal Windows Platform (UWP), Windows UI Library (WinUI), and .NET MAUI. The instructions for this tutorial are specific to creating a WPF .NET project using Visual Studio for Windows.
-
Start Visual Studio and create a new project.
- In the Visual Studio start screen, click Create a new project.
- Choose the WPF Application template for C#. If you don't see the template listed, you can find it by typing
WPinto the Search for templates text box.F Application - Click Next.
- Provide required values in the Configure your new project panel:
- Project name:
AccessServices With O Auth - Location:
choose a folder
- Project name:
- Click Next.
- Choose the framework:
.NE T 8.0 ( Long Term Support)
- Choose the framework:
- Click Create to create the project.
If you are developing with Visual Studio for Windows, ArcGIS Maps SDK for .NET provides a set of project templates for each supported .NET platform. These templates follow the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) design pattern. Install the ArcGIS Maps SDK for .NET Visual Studio Extension to add the templates to Visual Studio (Windows only). See Install and set up for details.
Add a reference to the API
-
Add a reference to the API by installing a NuGet package.
- In Solution Explorer, right-click Dependencies and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- In the NuGet Package Manager window, ensure the selected Package source is
nuget.org(upper-right). - Select the Browse tab and search for ArcGIS Maps SDK.
- In the search results, select the appropriate package for your platform. For this tutorial project, choose the Esri.ArcGISRuntime.WPF NuGet package.
- Confirm the Latest stable version of the package is selected in the Version dropdown.
- Click Apply.
- The Preview Changes dialog confirms any package(s) dependencies or conflicts. Review the changes and click OK to continue installing the packages.
- Review the license information on the License Acceptance dialog and click I Accept to add the package(s) to your project.
- In the Visual Studio Output window, ensure the packages were successfully installed. If you see an error about the target Windows version, you will fix that in the next step.
- Close the NuGet Package Manager window.
-
You may see an error like this in the Visual Studio Error List:
The '. If so, follow these steps to address it.Esri. ArcGIS Runtime. WP F' nuget package cannot be used to target 'net9.0-windows'. Target 'net9.0-windows10.0.19041.0' or later instead. - In Solution Explorer, right-click the project entry in the tree view and choose Edit Project File.
- Update the
<Targetelement withFramework > net9.0-windows10.0.19041.0(or higher).
Use dark colors for code blocks <PropertyGroup> <OutputType>WinExe</OutputType> <TargetFramework>net9.0-windows10.0.19041.0</TargetFramework> <UseWPF>true</UseWPF> </PropertyGroup>- Save the project file and close it.
Create a view model to store app logic
Following the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) design pattern, you'll create view model class to contain properties and methods that your view will bind to.
The Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) design pattern provides an architecture that separates user interface elements, and related code, from the underlying app logic. In this pattern,model represents the data consumed in an app, view represents the user interface, and view model contains the logic that binds model and view together. The framework required for such a pattern might initially seem like a lot of work for a small project, but as your project's complexity increases, a solid design foundation will make your code more flexible and easier to maintain.
In an ArcGIS app designed with MVVM, the map view or scene view usually provides the main view component. Many of the classes fill the role of model (representing data as maps, scenes, layers, graphics, features, and others). Much of the code you write will be for the view model component, where you will add logic to work with ArcGIS objects and provide data for display in the view.
-
Add a new class that will define a view model for the project.
- Click Project > Add Class ....
- Name the new class
Map.View Model.cs - Click Add to create the new class and add it to the project.
- The new class will open in Visual Studio.
-
Add required
usingstatements to the view model.MapViewModel.csUse dark colors for code blocks using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry; using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Mapping; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; -
Implement the
Iinterface in theNotify Property Changed Mapclass.View Model The
Iinterface defines aNotify Property Changed Propertyevent that will notify clients (views) that a property of the view model has changed. Bindings in the view will update to reflect the new value.Changed MapViewModel.csUse dark colors for code blocks namespace AccessServicesWithOAuth { class MapViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged { -
Inside the
Mapclass, add code to implement theView Model Propertyevent.Changed MapViewModel.csUse dark colors for code blocks class MapViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged { public event PropertyChangedEventHandler? PropertyChanged; protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = "") { PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } } -
Define a new property on the view model called
Mapthat exposes aMapobject. When the property is set, callOn.Property Changed MapViewModel.csUse dark colors for code blocks class MapViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged { public event PropertyChangedEventHandler? PropertyChanged; protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = "") { PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } private Map? _map; public Map? Map { get { return _map; } set { _map = value; OnPropertyChanged(); } } } -
Add a function to the
Mapclass calledView Model Setup. Start by creating a new map that uses a topographic basemap. Provide an initial viewpoint centered on the Santa Monica Mountains in California.Map MapViewModel.csUse dark colors for code blocks private Map? _map; public Map? Map { get { return _map; } set { _map = value; OnPropertyChanged(); } } private void SetupMap() { // Create a new map with a 'topographic vector' basemap. var trafficMap = new Map(BasemapStyle.ArcGISTopographic); // Set the initial viewpoint around the Santa Monica Mountains in California. var mapCenterPoint = new MapPoint(-118.805, 34.027, SpatialReferences.Wgs84); trafficMap.InitialViewpoint = new Viewpoint(mapCenterPoint, 100000); }You will add a layer to display the ArcGIS World Traffic service, a dynamic map service that presents historical and near real-time traffic information for different regions in the world. This is a secure service and requires an ArcGIS Online organizational subscription.
ArcGIS World Traffic service data is updated every five minutes to provide traffic speed and traffic incident visualization and identification.
Traffic speeds are displayed as a percentage of free-flow speeds, which is frequently the speed limit or how fast cars tend to travel when unencumbered by other vehicles. The streets are color coded as follows:
- Green (fast): 85 - 100% of free flow speeds
- Yellow (moderate): 65 - 85%
- Orange (slow); 45 - 65%
- Red (stop and go): 0 - 45%
-
Create an
ArcGISMapImageLayerto display the traffic service and add it to the map's collection of data layers (operational layers).MapViewModel.csUse dark colors for code blocks private void SetupMap() { // Create a new map with a 'topographic vector' basemap. var trafficMap = new Map(BasemapStyle.ArcGISTopographic); // Set the initial viewpoint around the Santa Monica Mountains in California. var mapCenterPoint = new MapPoint(-118.805, 34.027, SpatialReferences.Wgs84); trafficMap.InitialViewpoint = new Viewpoint(mapCenterPoint, 100000); // Create a layer to display the ArcGIS World Traffic service. var trafficServiceUrl = "https://traffic.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/World/Traffic/MapServer"; var trafficLayer = new ArcGISMapImageLayer(new Uri(trafficServiceUrl)); // Add the traffic layer to the map's data layer collection. trafficMap.OperationalLayers.Add(trafficLayer); } -
Set the view model's
Mapproperty. Data binding handles displaying the map in the view.MapViewModel.csUse dark colors for code blocks private void SetupMap() { // Create a new map with a 'topographic vector' basemap. var trafficMap = new Map(BasemapStyle.ArcGISTopographic); // Set the initial viewpoint around the Santa Monica Mountains in California. var mapCenterPoint = new MapPoint(-118.805, 34.027, SpatialReferences.Wgs84); trafficMap.InitialViewpoint = new Viewpoint(mapCenterPoint, 100000); // Create a layer to display the ArcGIS World Traffic service. var trafficServiceUrl = "https://traffic.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/World/Traffic/MapServer"; var trafficLayer = new ArcGISMapImageLayer(new Uri(trafficServiceUrl)); // Add the traffic layer to the map's data layer collection. trafficMap.OperationalLayers.Add(trafficLayer); // Set the view model Map property with the new map. this.Map = trafficMap; } -
Add a constructor to the class that calls
Setupwhen a newMap Mapis instantiated.View Model When you write code like
Map, the class constructor runs. This is a good place to add code that needs to run when the class is initialized.View Model new Map V M = new Map View Model(); MapViewModel.csUse dark colors for code blocks namespace AccessServicesWithOAuth { class MapViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged { public MapViewModel() { SetupMap(); }
Your Map is complete!
An advantage of using the MVVM design pattern is the ability to reuse code in a view model. Because this API has a nearly-standard API surface across platforms, a view model written for one app typically works on all supported .NET platforms. This view model could be used in a .NET MAUI app, a WinUI app, or a UWP app with little or no modification.
Set developer credentials
To allow your app users to access ArcGIS Location Services, use the developer credentials that you created in the Set up authentication step to authenticate requests for resources.
-
From the Visual Studio Project menu, choose Add class .... Name the class
ArcGISthen click Add. The new class is added to your project and opens in Visual Studio.Login Prompt.cs -
Select all the code in the new class and delete it.
-
Copy all of the code below and paste it into the
ArcGISclass in your project.Login Prompt.cs ArcGISLoginPrompt.csUse dark colors for code blocks Copy // Copyright 2021 Esri. // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at: http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an // "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific // language governing permissions and limitations under the License. using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Portal; using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Security; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Controls; using System.Windows.Navigation; using System.Windows.Threading; namespace UserAuth { internal static class ArcGISLoginPrompt { private const string ArcGISOnlineUrl = "https://www.arcgis.com/sharing/rest"; // Specify the Client ID and Redirect URL to use with OAuth authentication. // See the instructions here for creating OAuth app settings: // https://developers.arcgis.com/documentation/security-and-authentication/user-authentication/tutorials/create-oauth-credentials-user-auth/ private const string AppClientId = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID"; private const string OAuthRedirectUrl = "YOUR_REDIRECT_URL"; public static async Task<bool> EnsureAGOLCredentialAsync() { bool loggedIn = false; try { // Create the portal, prompting the user to log in if they haven't already. var portal = await ArcGISPortal.CreateAsync(new Uri(ArcGISOnlineUrl), loginRequired: true); // If the user logged in successfully, the portal's User property will be non-null. loggedIn = portal.User != null; } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // OAuth login was canceled, no need to display error to user. } catch (Exception ex) { // Login failure MessageBox.Show("Login failed: " + ex.Message); } return loggedIn; } public static void RegisterOAuthConfig() { var userConfig = new OAuthUserConfiguration(new Uri(ArcGISOnlineUrl), AppClientId, new Uri(OAuthRedirectUrl)); AuthenticationManager.Current.OAuthUserConfigurations.Add(userConfig); AuthenticationManager.Current.OAuthAuthorizeHandler = new OAuthAuthorize(); } #region OAuth handler // In a desktop (WPF) app, an IOAuthAuthorizeHandler component is used to handle some of the OAuth details. Specifically, it // implements AuthorizeAsync to show the login UI (generated by the server that hosts secure content) in a web control. // When the user logs in successfully, cancels the login, or closes the window without continuing, the IOAuthAuthorizeHandler // is responsible for obtaining the authorization from the server or raising an OperationCanceledException. public class OAuthAuthorize : IOAuthAuthorizeHandler { // Window to contain the OAuth UI. private Window? _authWindow; // Use a TaskCompletionSource to track the completion of the authorization. private TaskCompletionSource<IDictionary<string, string>> _tcs; // URL for the authorization callback result (the redirect URI configured for your application). private string _callbackUrl = ""; // URL that handles the OAuth request. private string? _authorizeUrl; // Function to handle authorization requests, takes the URIs for the secured service, the authorization endpoint, and the redirect URI. public Task<IDictionary<string, string>> AuthorizeAsync(Uri serviceUri, Uri authorizeUri, Uri callbackUri) { if (_tcs != null && !_tcs.Task.IsCompleted) throw new Exception("Task in progress"); _tcs = new TaskCompletionSource<IDictionary<string, string>>(); // Store the authorization and redirect URLs. _authorizeUrl = authorizeUri.AbsoluteUri; _callbackUrl = callbackUri.AbsoluteUri; // Call a function to show the login controls, make sure it runs on the UI thread for this app. Dispatcher dispatcher = Application.Current.Dispatcher; if (dispatcher == null || dispatcher.CheckAccess()) { AuthorizeOnUIThread(_authorizeUrl); } else { Action authorizeOnUIAction = () => AuthorizeOnUIThread(_authorizeUrl); dispatcher.BeginInvoke(authorizeOnUIAction); } // Return the task associated with the TaskCompletionSource. return _tcs.Task; } // Challenge for OAuth credentials on the UI thread. private void AuthorizeOnUIThread(string authorizeUri) { // Create a WebBrowser control to display the authorize page. WebBrowser webBrowser = new WebBrowser(); // Handle the navigation event for the browser to check for a response to the redirect URL. webBrowser.Navigating += WebBrowserOnNavigating; // Display the web browser in a new window. _authWindow = new Window { Content = webBrowser, Width = 450, Height = 450, WindowStartupLocation = WindowStartupLocation.CenterOwner }; // Set the app's window as the owner of the browser window (if main window closes, so will the browser). if (Application.Current != null && Application.Current.MainWindow != null) { _authWindow.Owner = Application.Current.MainWindow; } // Handle the window closed event then navigate to the authorize url. _authWindow.Closed += OnWindowClosed; webBrowser.Navigate(authorizeUri); // Display the window. _authWindow.ShowDialog(); } // Handle the browser window closing. private void OnWindowClosed(object? sender, EventArgs e) { // If the browser window closes, return the focus to the main window. if (_authWindow != null && _authWindow.Owner != null) { _authWindow.Owner.Focus(); } // If the task wasn't completed, the user must have closed the window without logging in. if (!_tcs.Task.IsCompleted) { // Set the task completion source exception to indicate a canceled operation. _tcs.SetCanceled(); } _authWindow = null; } // Handle browser navigation (content changing). private void WebBrowserOnNavigating(object sender, NavigatingCancelEventArgs e) { // Check for a response to the callback url. const string portalApprovalMarker = "/oauth2/approval"; WebBrowser? webBrowser = sender as WebBrowser; Uri uri = e.Uri; // If no browser, uri, or an empty url, return. if (webBrowser == null || uri == null || string.IsNullOrEmpty(uri.AbsoluteUri)) return; // Check for redirect. bool isRedirected = uri.AbsoluteUri.StartsWith(_callbackUrl) || _callbackUrl.Contains(portalApprovalMarker) && uri.AbsoluteUri.Contains(portalApprovalMarker); // Check if browser was redirected to the callback URL. (This indicates succesful authentication.) if (isRedirected) { e.Cancel = true; // Call a helper function to decode the response parameters. IDictionary<string, string> authResponse = DecodeParameters(uri); // Set the result for the task completion source. _tcs.SetResult(authResponse); // Close the window. if (_authWindow != null) { _authWindow.Close(); } } } private static IDictionary<string, string> DecodeParameters(Uri uri) { // Create a dictionary of key value pairs returned in an OAuth authorization response URI query string. string answer = ""; // Get the values from the URI fragment or query string. if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(uri.Fragment)) { answer = uri.Fragment.Substring(1); } else { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(uri.Query)) { answer = uri.Query.Substring(1); } } // Parse parameters into key / value pairs. Dictionary<string, string> keyValueDictionary = new Dictionary<string, string>(); string[] keysAndValues = answer.Split(new[] { '&' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); foreach (string kvString in keysAndValues) { string[] pair = kvString.Split('='); string key = pair[0]; string value = string.Empty; if (key.Length > 1) { value = Uri.UnescapeDataString(pair[1]); } keyValueDictionary.Add(key, value); } // Return the dictionary of string keys/values. return keyValueDictionary; } } #endregion OAuth handler } } -
Add your values for the client ID (
App) and for the redirect URL (Client Id O). These are the user authentication settings you created in the Set up authentication step.Auth Redirect Url ArcGISLoginPrompt.csUse dark colors for code blocks internal static class ArcGISLoginPrompt { private const string ArcGISOnlineUrl = "https://www.arcgis.com/sharing/rest"; // Specify the Client ID and Redirect URL to use with OAuth authentication. // See the instructions here for creating OAuth app settings: // https://developers.arcgis.com/documentation/security-and-authentication/user-authentication/tutorials/create-oauth-credentials-user-auth/ private const string AppClientId = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID"; private const string OAuthRedirectUrl = "YOUR_REDIRECT_URL"; -
In the Solution Explorer, expand the node for App.xaml, and double-click App.xaml.cs to open it.
-
In the App class, add an override for the
Onfunction to call theStartup() Setmethod on your staticChallenge Handler() ArcGISclass.Login Prompt App.xaml.csUse dark colors for code blocks public partial class App : Application { protected override void OnStartup(StartupEventArgs e) { base.OnStartup(e); // Call a function to set up the AuthenticationManager for OAuth. UserAuth.ArcGISLoginPrompt.RegisterOAuthConfig(); } } } -
Save and close the
App.xaml.csfile.
Best Practice: The OAuth credentials are stored directly in the code as a convenience for this tutorial. Do not store credentials directly in source code in a production environment.
Next, you will set up a view in your project to consume the view model.
Add a map view
A MapView control is used to display a map. You will add a map view to your project UI and use data binding to consume the value of the Map property defined on Map.
-
Add required XML namespace and resource declarations.
- Open
Mainand switch to the XAML viewWindow.xaml - Inside the existing namespace declarations, add an
esriXML namespace for the ArcGIS controls - Add XAML that defines a
Mapinstance as a static resourceView Model
MainWindow.xamlUse dark colors for code blocks <Window x:Class="AccessServicesWithOAuth.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AccessServicesWithOAuth" xmlns:esri="http://schemas.esri.com/arcgis/runtime/2013" mc:Ignorable="d" Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800"> <Window.Resources> <local:MapViewModel x:Key="MapViewModel" /> </Window.Resources> - Open
-
Add a
MapViewcontrol toMainand bind it to theWindow.xaml Map.View Model - Add XAML that defines a
Mapcontrol namedView MainMap View - Use data binding to set the
Mapproperty of the control using theMapresource.View Model
MainWindow.xamlUse dark colors for code blocks <Grid> <esri:MapView x:Name="MainMapView" Map="{Binding Map, Source={StaticResource MapViewModel}}" /> </Grid> - Add XAML that defines a
Run the app
Click Debug > Start Debugging (or press <F5> on the keyboard) to run the app.
You will be prompted for a username and password. Once you authenticate successfully, you will see a traffic map centered on the Santa Monica Mountains in California.

Alternatively, you can download the tutorial solution, as follows.
Option 2: Download the solution
-
Click the Download solution link in the right-hand panel of the page.
-
Unzip the file to a location on your machine.
-
Open the
.slnfile in Visual Studio.
Since the downloaded solution does not contain authentication credentials, you must add the developer credentials that you created in the Set up authentication section.
Set developer credentials in the solution
To allow your app users to access ArcGIS location services, use the developer credentials that you created in the Set up authentication step to authenticate requests for resources.
-
From the Visual Studio Solution explorer window, open the
ArcGISfile.Login Prompt.cs -
Set your values for the client ID (
O) and the redirect URL (Auth Client ID O). These are the user authentication settings you created in the Set up authentication step.Auth Redirect Url ArcGISLoginPrompt.csUse dark colors for code blocks internal static class ArcGISLoginPrompt { private const string ArcGISOnlineUrl = "https://www.arcgis.com/sharing/rest"; // Specify the Client ID and Redirect URL to use with OAuth authentication. // See the instructions here for creating OAuth app settings: // https://developers.arcgis.com/documentation/security-and-authentication/user-authentication/tutorials/create-oauth-credentials-user-auth/ private const string AppClientId = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID"; private const string OAuthRedirectUrl = "YOUR_REDIRECT_URL";
Best Practice: The OAuth credentials are stored directly in the code as a convenience for this tutorial. Do not store credentials directly in source code in a production environment.
Run the app
Click Debug > Start Debugging (or press <F5> on the keyboard) to run the app.
You will be prompted for a username and password. Once you authenticate successfully, you will see a traffic map centered on the Santa Monica Mountains in California.

Additional resources
If you are implementing OAuth for another .NET platform, you might find some of the following resources helpful.
- ArcGIS Maps SDK for .NET OAuth sample: The WPF version of this sample uses code similar to code used in this tutorial. The sample is available for other .NET platforms (use the switcher control at the top of the page) to illustrate implementing OAuth for apps targeting WinUI, UWP, and .NET MAUI.
- Web authentication broker: Use this authentication broker to implement OAuth in your Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps.