Display KML from a URL, portal item, or local KML file.
Use case
Keyhole Markup Language (KML) is a data format used by Google Earth. KML is popular as a transmission format for consumer use and for sharing geographic data between apps. You can use Runtime to display KML files, with full support for a variety of features, including network links, 3D models, screen overlays, and tours.
How to use the sample
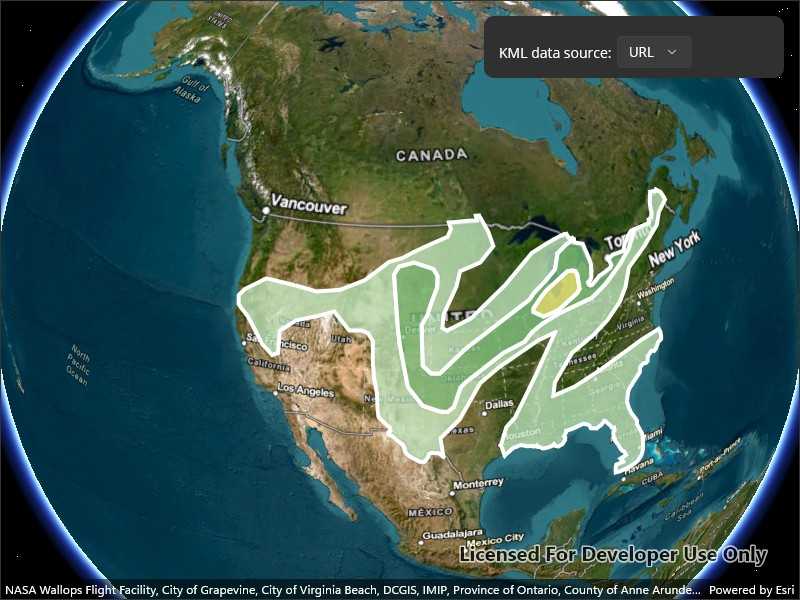
Use the UI to select a source. A KML file from that source will be loaded and displayed in the scene.
How it works
- To create a KML layer from a URL, create a
KmlDatasetusing the URL to the KML file. Then pass the dataset to theKmlLayerconstructor. - To create a KML layer from a portal item, construct a
PortalItemwith aPortaland the KML portal item ID. Pass the portal item to theKmlLayerconstructor. - To create a KML layer from a local file, create a
KmlDatasetusing the absolute file path to the local KML file. Then pass the dataset to theKmlLayerconstructor. - Add the layer as an operational layer to the scene with
scene.OperationalLayers.Add(kmlLayer).
Relevant API
- KmlDataset
- KmlLayer
Offline data
| Link | Local Location |
|---|---|
| US State Capitals | <userhome>/ArcGIS/Runtime/Data/kml/US_State_Capitals.kml |
About the data
This sample displays three different KML files:
- From URL - this is a map of the convective outlook produced by NOAA/NWS Storm Prediction Center. It uses KML network links to always show the latest data.
- From local file - this is a map of U.S. state capitals. It doesn't define an icon, so the default pushpin is used for the points.
- From portal item - this is a map of U.S. states.
Tags
keyhole, KML, KMZ, OGC
Sample Code
// Copyright 2022 Esri.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at: http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an
// "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific
// language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
using ArcGIS.Samples.Managers;
using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry;
using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Mapping;
using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Portal;
namespace ArcGIS.Samples.DisplayKml
{
[ArcGIS.Samples.Shared.Attributes.Sample(
name: "Display KML",
category: "Layers",
description: "Display KML from a URL, portal item, or local KML file.",
instructions: "Use the UI to select a source. A KML file from that source will be loaded and displayed in the scene.",
tags: new[] { "KML", "KMZ", "OGC", "keyhole" })]
[ArcGIS.Samples.Shared.Attributes.OfflineData("324e4742820e46cfbe5029ff2c32cb1f")]
public partial class DisplayKml : ContentPage
{
private readonly Envelope _usEnvelope = new Envelope(-144.619561355187, 18.0328662832097, -66.0903762761083, 67.6390975806745, SpatialReferences.Wgs84);
private readonly string[] _sources = { "URL", "Local file", "Portal item" };
public DisplayKml()
{
InitializeComponent();
Initialize();
}
private void Initialize()
{
// Set up the basemap.
MySceneView.Scene = new Scene(BasemapStyle.ArcGISImagery);
// Update the UI.
LayerPicker.IsEnabled = true;
LayerPicker.ItemsSource = _sources;
LayerPicker.SelectedIndexChanged += LayerPicker_SelectionChanged;
LayerPicker.SelectedIndex = 0;
}
private async void LayerPicker_SelectionChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Clear existing layers.
MySceneView.Scene.OperationalLayers.Clear();
// Get the name of the selected layer.
string name = _sources[LayerPicker.SelectedIndex];
try
{
// Create the layer using the chosen constructor.
KmlLayer layer;
switch (name)
{
case "URL":
default:
layer = new KmlLayer(new Uri("https://www.spc.noaa.gov/products/outlook/SPC_outlooks.kml"));
break;
case "Local file":
string filePath = DataManager.GetDataFolder("324e4742820e46cfbe5029ff2c32cb1f", "US_State_Capitals.kml");
layer = new KmlLayer(new Uri(filePath));
break;
case "Portal item":
ArcGISPortal portal = await ArcGISPortal.CreateAsync();
PortalItem item = await PortalItem.CreateAsync(portal, "9fe0b1bfdcd64c83bd77ea0452c76253");
layer = new KmlLayer(item);
break;
}
// Add the selected layer to the map.
MySceneView.Scene.OperationalLayers.Add(layer);
// Zoom to the extent of the United States.
await MySceneView.SetViewpointAsync(new Viewpoint(_usEnvelope));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
await Application.Current.Windows[0].Page.DisplayAlert("Error", ex.ToString(), "OK");
}
}
}
}