Apply a hillshade renderer to a raster.

Use case
An environmental agency may track coastal erosion by comparing images of an area taken over a longer period of time with hillshade renderers applied.
How to use the sample
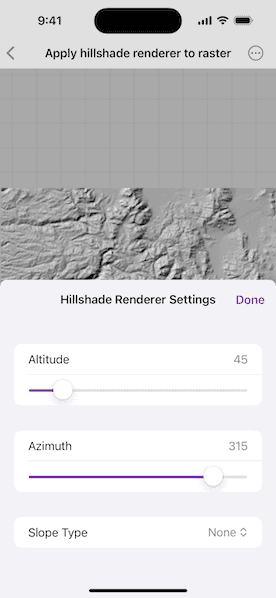
Choose and adjust the settings to update the hillshade renderer on the raster layer. The sample allows you to change the Altitude, Azimuth, and Slope Type.
How it works
- Create a
Rasterfrom a grayscale raster file. - Create a
RasterLayerfrom the raster. - Create a
Basemapfrom the raster layer and set it to the map. - Create a
HillshadeRenderer, specifying the altitude, azimuth, slope type and other properties. - Set the hillshade renderer to be used on the raster layer.
Relevant API
- Basemap
- HillshadeRenderer
- Raster
- RasterLayer
Tags
altitude, angle, azimuth, raster, slope, visualization
Sample Code
// Copyright 2025 Esri
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
import ArcGIS
import SwiftUI
struct ApplyHillshadeRendererToRasterView: View {
/// The model used to store the geo model and other expensive objects
/// used in this view.
class Model: ObservableObject {
/// The map that will be shown.
let map: Map
/// The raster layer in the map.
private let rasterLayer: RasterLayer
/// The raster renderer.
var renderer: HillshadeRenderer {
didSet {
// When the renderer is updated, update the layer accordingly.
rasterLayer.renderer = renderer
}
}
init() {
// Gets the raster file URL.
let rasterFileURL = Bundle.main.url(forResource: "srtm", withExtension: "tiff", subdirectory: "srtm/srtm hillshade raster")!
// Creates a raster with the file URL.
let raster = Raster(fileURL: rasterFileURL)
// Creates a raster layer using the raster object.
rasterLayer = RasterLayer(raster: raster)
// Apply the hillshade renderer to the raster layer.
renderer = HillshadeRenderer(
altitude: 45,
azimuth: 315,
slopeType: nil,
zFactor: 0.000016,
pixelSizeFactor: 1,
pixelSizePower: 1,
outputBitDepth: 8
)
rasterLayer.renderer = renderer
// Create our map.
map = Map(basemap: .init(baseLayer: rasterLayer))
}
}
/// The view model for the sample.
@StateObject private var model = Model()
/// A Boolean value indicating if the settings panel is presented.
@State private var isSettingsPanelPresented = false
var body: some View {
// Creates a map view to display the map.
MapView(map: model.map)
.toolbar {
ToolbarItem(placement: .bottomBar) {
Button("Settings") {
isSettingsPanelPresented = true
}
.popover(isPresented: $isSettingsPanelPresented) {
SettingsView(renderer: $model.renderer)
.presentationDetents([.medium])
.frame(idealWidth: 320, idealHeight: 380)
}
}
}
}
}