Use annotation sublayers to gain finer control of annotation layer subtypes.
Use case
Annotation, which differs from labels by having a fixed place and size, is typically only relevant at particular scales. Annotation sublayers allow for finer control of annotation by allowing properties (like visibility in the map and legend) to be set and others to be read (like name) on subtypes of an annotation layer.
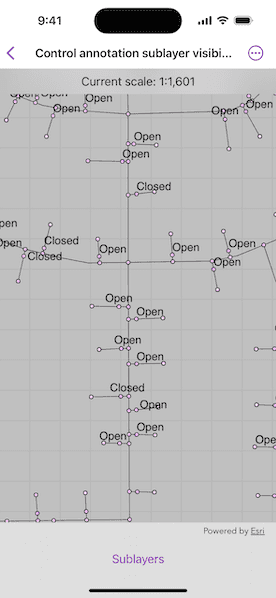
An annotation dataset which marks valves as "Opened" or "Closed", might be set to display the "Closed" valves over a broader range of scales than the "Opened" valves, if the "Closed" data is considered more relevant by the map's author. Regardless, the user can be given a manual option to set visibility of annotation sublayers on and off, if required.
How to use the sample
Start the sample and take note of the visibility of the annotation. Zoom in and out to see the annotation turn on and off based on scale ranges set on the data.
Use the toggles to manually set "Open" and "Closed" annotation sublayers visibility to on or off.
How it works
- Load a
MobileMapPackagethat contains anAnnotationLayer. - Get the sublayers from the map package's layers by calling
AnnotationLayer.subLayerContents[i]. - You can toggle the visibility of each sublayer manually setting sublayer's
isVisibleproperty. - To determine if a sublayer is visible at the current scale of the MapView, use
AnnotationSublayer.isVisible(atScale:), by passing in the map's current scale.
Relevant API
- AnnotationLayer
- AnnotationSublayer
- LayerContent
Offline data
This sample downloads the GasDeviceAnno mobile map package from ArcGIS Online automatically.
About the data
The scale ranges were set by the map's author using ArcGIS Pro:
- The "Open" annotation sublayer has its maximum scale set to 1:500 and its minimum scale set to 1:2000.
- The "Closed" annotation sublayer has no minimum or maximum scales set, so will be drawn at all scales.
Tags
annotation, scale, text, utilities, visualization
Sample Code
// Copyright 2025 Esri
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
import ArcGIS
import SwiftUI
struct ControlAnnotationSublayerVisibilityView: View {
/// The view model for the sample.
@State private var model = Model()
/// The error shown in the error alert.
@State private var error: (any Error)?
var body: some View {
MapView(map: model.map)
.onScaleChanged { scale in
model.currentScale = scale
}
.overlay(alignment: .top) {
Text("Current scale: \(model.currentScaleText)")
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, alignment: .center)
.padding(8)
.background(.ultraThinMaterial, ignoresSafeAreaEdges: .horizontal)
.multilineTextAlignment(.center)
}
.toolbar {
ToolbarItem(placement: .bottomBar) {
Menu("Sublayers") {
Toggle("Closed", isOn: $model.showsClosedSublayer)
.onChange(of: model.showsClosedSublayer) {
model.setClosedSublayerVisibility(model.showsClosedSublayer)
}
Toggle(model.minMaxScaleText, isOn: $model.showsOpenSublayer)
.onChange(of: model.showsOpenSublayer) {
model.setOpenSublayerVisibility(model.showsOpenSublayer)
}
.disabled(!model.visibleAtCurrentExtent)
}
}
}
.task {
do {
try await model.loadMobileMapPackage()
} catch {
self.error = error
}
}
.errorAlert(presentingError: $error)
}
}
#Preview {
ControlAnnotationSublayerVisibilityView()
}