Query data using a time extent.
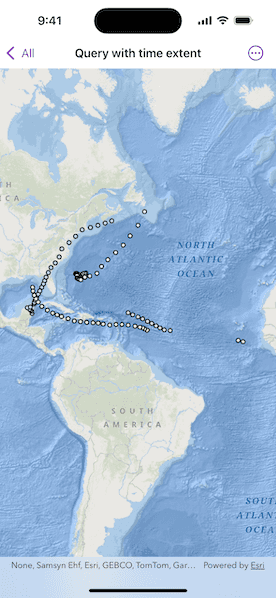
Use case
This workflow can be used to return records that are between a specified start and end date. For example, records of Canada goose sightings over time could be queried to only show sightings during the winter migration time period.
How to use the sample
Run the sample, and a subset of records will be displayed on the map.
How it works
- Create a
ServiceFeatureTablefrom a URL of a time-enabled service. Time-enabled services will have TimeInfo defined in the service description. This information is specified in ArcMap or ArcGIS Pro prior to publishing the service. - Set the feature table's
featureRequestModeproperty tomanualCache, so that the developer can control how and when the feature table is populated with data. - Create a
FeatureLayerwith the feature table and add it to a map's operational layers to display it. - Create a
TimeExtentobject usingDateobjects for the start time and end time being queried. - Create a default
QueryParametersobject and set the parameter'stimeExtentproperty. - Populate the feature table using
ServiceFeatureTable.populateFromService(using:clearCache:outFields:)with the custom query parameters created in the previous steps. - The feature table is populated with data that matches the provided query.
Relevant API
- QueryParameters
- ServiceFeatureTable.populateFromService(using:clearCache:outFields:)
- TimeExtent
About the data
This sample uses Atlantic hurricane data from the year 2000. The data is from the National Hurricane Center (NOAA / National Weather Service).
Tags
query, time, time extent
Sample Code
QueryWithTimeExtentView.swift
// Copyright 2025 Esri
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
import ArcGIS
import SwiftUI
struct QueryWithTimeExtentView: View {
/// A map with an ocean basemap style.
@State private var map: Map = {
let map = Map(basemapStyle: .arcGISOceans)
// Sets the initial viewpoint of the map.
map.initialViewpoint = Viewpoint(latitude: 20.0, longitude: -55.0, scale: 9e7)
return map
}()
/// The error shown in the error alert.
@State private var error: (any Error)?
var body: some View {
MapView(map: map)
.task {
do {
let featureTable = ServiceFeatureTable(url: .hurricanesService)
// Sets the feature request mode to manual (only manual is currently
// supported). In this mode, you must manually populate the table -
// panning and zooming won't request features automatically.
featureTable.featureRequestMode = .manualCache
let layer = FeatureLayer(featureTable: featureTable)
map.addOperationalLayer(layer)
try await populateFeatures(from: featureTable)
} catch {
self.error = error
}
}
}
/// Populates the service feature table using queried features.
/// - Parameter featureTable: The service feature table.
private func populateFeatures(from featureTable: ServiceFeatureTable) async throws {
// Creates parameters to query for features within the time extent.
let queryParameters = QueryParameters()
let timeExtent = TimeExtent(startDate: .startDate, endDate: .endDate)
queryParameters.timeExtent = timeExtent
_ = try await featureTable.populateFromService(
using: queryParameters,
clearCache: false,
outFields: ["*"]
)
}
}
private extension Date {
static let startDate = Calendar.current.date(from: DateComponents(year: 2000, month: 9, day: 1))!
static let endDate = Calendar.current.date(from: DateComponents(year: 2000, month: 9, day: 22))!
}
private extension URL {
static var hurricanesService: URL {
URL(string: "https://sampleserver6.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/rest/services/Hurricanes/MapServer/0")!
}
}
#Preview {
QueryWithTimeExtentView()
}