Calculate a geodesic path between two points and measure its distance.
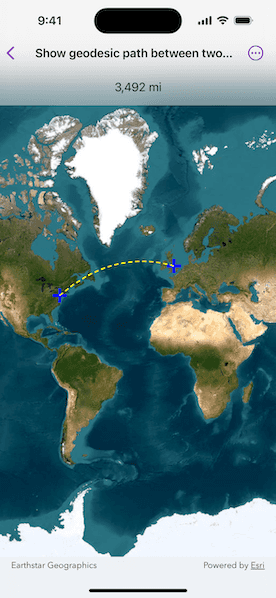
Use case
A geodesic distance provides an accurate, real-world distance between two points. Visualizing flight paths between cities is a common example of a geodesic operation since the flight path between two airports takes into account the curvature of the earth, rather than following the planar path between those points, which appears as a straight line on a projected map.
How to use the sample
Click anywhere on the map. A line graphic will display the geodesic line between the two points. In addition, text that indicates the geodesic distance between the two points will be updated. Click elsewhere and a new line will be created.
How it works
- Create a
Pointand display it as aGraphicwhen theMapViewis tapped. - Obtain a new point when another tap occurs on the
MapViewand add this point as a graphic. - Create a
Polylinefrom the two points. - Execute
GeometryEngine.geodeticDensify(_:maxSegmentLength:lengthUnit:curveType:)by passing in the created polyline then create a graphic from the returnedGeometry. - Execute
GeometryEngine.geodeticDistance(from:to:distanceUnit:azimuthUnit:curveType:)by passing in the two points and display the returned length on the screen.
Relevant API
- GeometryEngine.geodeticDensify(_:maxSegmentLength:lengthUnit:curveType:)
- GeometryEngine.geodeticDistance(from:to:distanceUnit:azimuthUnit:curveType:)
- MapView.onSingleTapGesture(perform:)
About the data
The Imagery basemap provides the global context for the displayed geodesic line.
Tags
densify, distance, geodesic, geodetic
Sample Code
// Copyright 2025 Esri
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
import ArcGIS
import SwiftUI
struct ShowGeodesicPathBetweenTwoPointsView: View {
/// The map that will be displayed in the map view.
@State private var map = Map(basemapStyle: .arcGISImageryStandard)
/// The graphics overlay that will be displayed on the map view.
/// This will hold the graphics that show the start point, end point,
/// and geodesic path.
@State private var overlay = GraphicsOverlay()
/// The current measurement state.
@State private var state: MeasurementState = .notStarted
/// The symbology for point graphics.
private let pointSymbol: Symbol = SimpleMarkerSymbol(style: .cross, color: .blue, size: 20)
/// The symbology for the line graphic.
private let lineSymbol: Symbol = SimpleLineSymbol(style: .dash, color: .yellow, width: 2)
var body: some View {
MapView(map: map, graphicsOverlays: [overlay])
.onSingleTapGesture { _, mapPoint in
state = switch state {
case .notStarted, .complete:
// If the state is empty or complete, then start a new
// path, adding the tap point as the first graphic.
.startOnly(start: mapPoint)
case .startOnly(let start):
// If the state was started, then add the end point
// to complete it.
.complete(start: start, end: mapPoint)
}
}
.overlay(alignment: .top) {
Group {
switch state {
case .notStarted, .startOnly:
Text("Tap on the map to show a geodesic path")
case .complete(_, _, _, let length):
Text(length, format: .measurement(width: .abbreviated))
}
}
.padding()
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity)
.background(.ultraThinMaterial)
}
.onChange(of: state) { updateGraphicsOverlay() }
.animation(.default, value: state)
}
/// Update the graphics overlay for the current state.
private func updateGraphicsOverlay() {
overlay.removeAllGraphics()
switch state {
case .notStarted:
break
case .startOnly(let start):
overlay.addGraphic(Graphic(geometry: start, symbol: pointSymbol))
case .complete(let start, let end, let line, _):
overlay.addGraphic(Graphic(geometry: start, symbol: pointSymbol))
overlay.addGraphic(Graphic(geometry: end, symbol: pointSymbol))
overlay.addGraphic(Graphic(geometry: line, symbol: lineSymbol))
}
}
}
extension ShowGeodesicPathBetweenTwoPointsView {
/// A value that represents the measurement state of the view.
enum MeasurementState: Equatable {
/// No measurement started.
case notStarted
/// Only have a starting point.
case startOnly(start: Point)
/// Completed measurement.
case complete(start: Point, end: Point, line: Polyline, distance: Measurement<UnitLength>)
/// Creates a `complete` measurement state with a start and end point,
/// calculating the line and length.
static func complete(start: Point, end: Point) -> Self {
// Create a geodesic line from the start, end points.
let geodesicLine = GeometryEngine.geodeticDensify(
Polyline(points: [start, end]),
maxSegmentLength: 1,
lengthUnit: .kilometers,
curveType: .geodesic
) as! Polyline
// Calculate the geodesic distance between the two points.
let geodesicDistance = GeometryEngine.geodeticDistance(
from: start,
to: end,
distanceUnit: .meters,
azimuthUnit: .degrees,
curveType: .geodesic
)!
return complete(
start: start,
end: end,
line: geodesicLine,
distance: geodesicDistance.distance
)
}
}
}
#Preview {
ShowGeodesicPathBetweenTwoPointsView()
}