Find the union, intersection, or difference of two geometries.
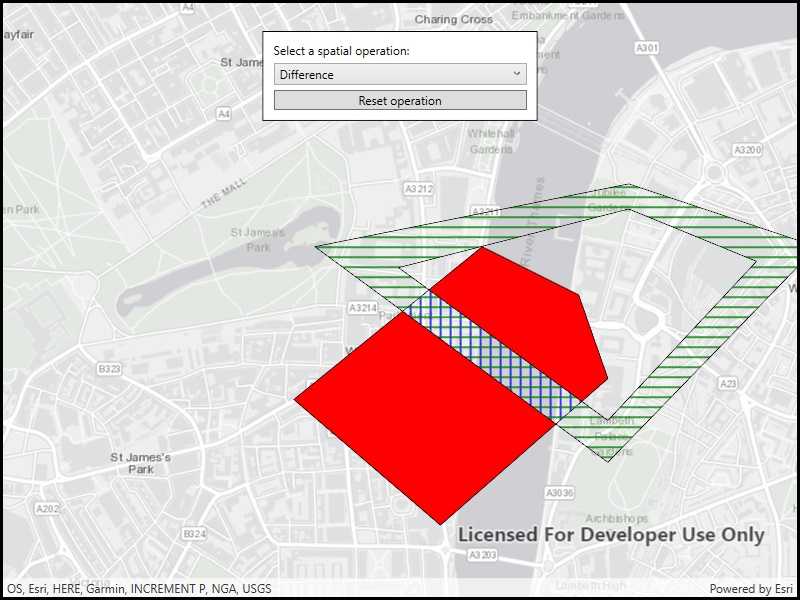
Use case
The different spatial operations (union, difference, symmetric difference, and intersection) can be used for a variety of spatial analyses. For example, government authorities may use the intersect operation to determine whether a proposed road cuts through a restricted piece of land such as a nature reserve or a private property. When these operations are chained together, they become even more powerful. An analysis of food deserts within an urban area might begin by union-ing service areas of grocery stores, farmer's markets, and food co-ops. Taking the difference between this single geometry of all services areas and that of a polygon delineating a neighborhood would reveal the areas within that neighborhood where access to healthy, whole foods may not exist.
How to use the sample
The sample provides an option to select a spatial operation. When an operation is selected, the resulting geometry is shown in red. The 'reset operation' button undoes the action and allow selecting a different operation.
How it works
- Create a
GraphicsOverlayand add it to theMapView. - Define a
PointCollectionof eachGeometry. - Add the overlapping polygons to the graphics overlay.
- Perform spatial relationships between the polygons by using the appropriate operation:
geometry1.Union(geometry2)- This method returns the two geometries united together as one geometry.geometry1.Difference(geometry2)- This method returns any part of Geometry2 that does not intersect Geometry1.geometry1.SymmetricDifference(geometry2)- This method returns any part of Geometry1 or Geometry2 which do not intersect.geometry1.Intersection(geometry2)- This method returns the intersection of Geometry1 and Geometry2.
- Use the geometry that is returned from the method call to create a new
Graphicand add it to the graphics overlay for it to be displayed.
Relevant API
- Geometry
- GeometryEngine
- GeometryEngine.Difference
- GeometryEngine.Intersection
- GeometryEngine.SymmetricDifference
- GeometryEngine.Union
- Graphic
- GraphicsOverlay
Tags
analysis, combine, difference, geometry, intersection, merge, polygon, union
Sample Code
// Copyright 2018 Esri.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at: http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an
// "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific
// language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry;
using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Mapping;
using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Symbology;
using Esri.ArcGISRuntime.UI;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows;
namespace ArcGIS.WPF.Samples.SpatialOperations
{
[ArcGIS.Samples.Shared.Attributes.Sample(
name: "Perform spatial operations",
category: "Geometry",
description: "Find the union, intersection, or difference of two geometries.",
instructions: "The sample provides an option to select a spatial operation. When an operation is selected, the resulting geometry is shown in red. The 'reset operation' button undoes the action and allow selecting a different operation.",
tags: new[] { "analysis", "combine", "difference", "geometry", "intersection", "merge", "polygon", "union" })]
public partial class SpatialOperations
{
// GraphicsOverlay to hold the polygon graphics.
private GraphicsOverlay _polygonsOverlay;
// Polygon graphics to run spatial operations on.
private Graphic _graphicOne;
private Graphic _graphicTwo;
// Graphic to display the spatial operation result polygon.
private Graphic _resultGraphic;
public SpatialOperations()
{
InitializeComponent();
// Create the map, set the initial extent, and add the polygon graphics.
Initialize();
}
private void Initialize()
{
// Create the map with a gray canvas basemap and an initial location centered on London, UK.
Map spatialOperationsMap = new Map(BasemapStyle.ArcGISLightGray);
spatialOperationsMap.InitialViewpoint = new Viewpoint(51.5017, -0.12714, 20000);
// Add the map to the map view.
MyMapView.Map = spatialOperationsMap;
// Create and add two overlapping polygon graphics to operate on.
CreatePolygonsOverlay();
// Fill the combo box with some spatial operations to run on the polygon graphics.
SpatialOperationComboBox.Items.Add("Difference");
SpatialOperationComboBox.Items.Add("Intersection");
SpatialOperationComboBox.Items.Add("Symmetric difference");
SpatialOperationComboBox.Items.Add("Union");
}
// Handle the spatial operation selection by performing the operation and showing the result polygon.
private void SpatialOperationComboBox_SelectionChanged(object sender, System.Windows.Controls.SelectionChangedEventArgs e)
{
// If an operation hasn't been selected, return.
if (SpatialOperationComboBox.SelectedItem == null) { return; }
// Remove any currently displayed result.
_polygonsOverlay.Graphics.Remove(_resultGraphic);
// Polygon geometry from the input graphics.
Geometry polygonOne = _graphicOne.Geometry;
Geometry polygonTwo = _graphicTwo.Geometry;
// Result polygon for spatial operations.
Geometry resultPolygon = null;
// Run the selected spatial operation on the polygon graphics and get the result geometry.
string operation = (string)SpatialOperationComboBox.SelectedItem;
switch (operation)
{
case "Union":
resultPolygon = polygonOne.Union(polygonTwo);
break;
case "Difference":
resultPolygon = polygonOne.Difference(polygonTwo);
break;
case "Symmetric difference":
resultPolygon = polygonOne.SymmetricDifference(polygonTwo);
break;
case "Intersection":
resultPolygon = polygonOne.Intersection(polygonTwo);
break;
}
// Create a black outline symbol to use for the result polygon.
SimpleLineSymbol outlineSymbol = new SimpleLineSymbol(SimpleLineSymbolStyle.Solid, System.Drawing.Color.Black, 1);
// Create a solid red fill symbol for the result polygon graphic.
SimpleFillSymbol resultSymbol = new SimpleFillSymbol(SimpleFillSymbolStyle.Solid, System.Drawing.Color.Red, outlineSymbol);
// Create the result polygon graphic and add it to the graphics overlay.
_resultGraphic = new Graphic(resultPolygon, resultSymbol);
_polygonsOverlay.Graphics.Add(_resultGraphic);
}
private void ResetOperationButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Remove any currently displayed result.
_polygonsOverlay.Graphics.Remove(_resultGraphic);
// Clear the selected spatial operation.
SpatialOperationComboBox.SelectedIndex = -1;
}
private void CreatePolygonsOverlay()
{
// Create a black outline symbol to use for the polygons.
SimpleLineSymbol outlineSymbol = new SimpleLineSymbol(SimpleLineSymbolStyle.Solid, System.Drawing.Color.Black, 1);
// Create a point collection to define polygon vertices.
PointCollection polygonVertices = new PointCollection(SpatialReferences.WebMercator)
{
new MapPoint(-13960, 6709400),
new MapPoint(-14660, 6710000),
new MapPoint(-13760, 6710730),
new MapPoint(-13300, 6710500),
new MapPoint(-13160, 6710100)
};
// Create a polygon graphic with a blue fill.
SimpleFillSymbol fillSymbol = new SimpleFillSymbol(SimpleFillSymbolStyle.Vertical, System.Drawing.Color.Blue, outlineSymbol);
Polygon polygonOne = new Polygon(polygonVertices);
_graphicOne = new Graphic(polygonOne, fillSymbol);
// Create a point collection to define outer polygon ring vertices.
PointCollection outerRingVerticesCollection = new PointCollection(SpatialReferences.WebMercator)
{
new MapPoint(-13060, 6711030),
new MapPoint(-12160, 6710730),
new MapPoint(-13160, 6709700),
new MapPoint(-14560, 6710730)
};
// Create a point collection to define inner polygon ring vertices ("donut hole").
PointCollection innerRingVerticesCollection = new PointCollection(SpatialReferences.WebMercator)
{
new MapPoint(-13060, 6710910),
new MapPoint(-14160, 6710630),
new MapPoint(-13160, 6709900),
new MapPoint(-12450, 6710660)
};
// Create a list to contain the inner and outer ring point collections.
List<PointCollection> polygonParts = new List<PointCollection>
{
outerRingVerticesCollection,
innerRingVerticesCollection
};
// Create a polygon graphic with a green fill.
fillSymbol = new SimpleFillSymbol(SimpleFillSymbolStyle.Horizontal, System.Drawing.Color.Green, outlineSymbol);
_graphicTwo = new Graphic(new Polygon(polygonParts), fillSymbol);
// Create a graphics overlay in the map view to hold the polygons.
_polygonsOverlay = new GraphicsOverlay();
MyMapView.GraphicsOverlays.Add(_polygonsOverlay);
// Add the polygons to the graphics overlay.
_polygonsOverlay.Graphics.Add(_graphicOne);
_polygonsOverlay.Graphics.Add(_graphicTwo);
}
}
}